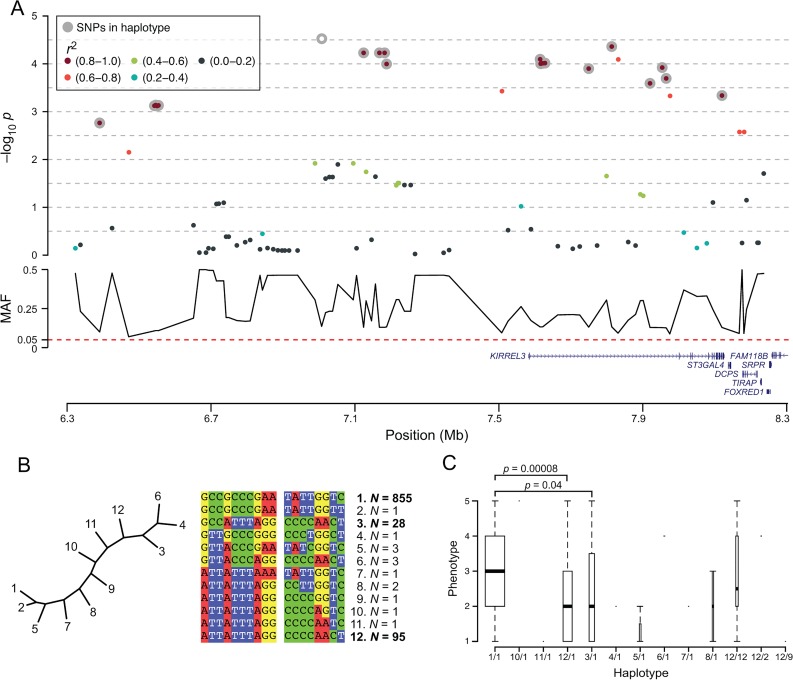
Fig 2. Two risk haplotypes at the German shepherd CFA5 locus results in lower IgA levels.
(A) The genome wide significant locus on CFA5 consisted of 17 SNPs (grey circles) in LD (r2 >0.8) with the top SNP (white), with only the KIRREL3 gene within the associated region and six genes adjacent. (B) The 18 SNPs were phased into 12 different haplotypes, of which nine were rare (N <3). Haplotype 1 was the most common (N = 855) and the remaining two haplotypes; 12 and 3 were more similar to each other than to haplotype 1. (C) Dogs homozygous for haplotype 1 (1/1) represented all groups of IgA evenly, whereas dogs heterozygous 1/12 and 1/3 had significantly lower IgA levels compared to 1/1 (p = 0.04 and 0.0008, respectively).