Abstract
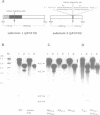
Two homologous group I introns, the second intron of the cyt b gene, from related Saccharomyces species differ in their mobility. The S.capensis intron is mobile and encodes the I-ScaI endonuclease promoting intron homing, whilst the homologous S.cerevisiae intron is not mobile, but functions as an RNA maturase promoting splicing. These two intron-encoded proteins differ by only four amino acid substitutions. Taking advantage of the remarkable similarity of the two intron open reading frames and using biolistic transformation of mitochondria, we show that the replacement of only two non-adjacent residues in the S.cerevisiae maturase carboxy-terminal sequence is sufficient to induce a homing-endonuclease activity without losing the splicing function. Also, we demonstrate that these two activities reside in the S.capensis bi2-encoded protein which functions in both splicing and intron mobility in the wild-type cells. These results provide new insight into our understanding of the activity and the evolution of group I intron-encoded proteins.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anziano P. Q., Hanson D. K., Mahler H. R., Perlman P. S. Functional domains in introns: trans-acting and cis-acting regions of intron 4 of the cob gene. Cell. 1982 Oct;30(3):925–932. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90297-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banroques J., Delahodde A., Jacq C. A mitochondrial RNA maturase gene transferred to the yeast nucleus can control mitochondrial mRNA splicing. Cell. 1986 Sep 12;46(6):837–844. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90065-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banroques J., Perea J., Jacq C. Efficient splicing of two yeast mitochondrial introns controlled by a nuclear-encoded maturase. EMBO J. 1987 Apr;6(4):1085–1091. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04862.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cech T. R. Self-splicing of group I introns. Annu Rev Biochem. 1990;59:543–568. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.59.070190.002551. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colleaux L., d'Auriol L., Betermier M., Cottarel G., Jacquier A., Galibert F., Dujon B. Universal code equivalent of a yeast mitochondrial intron reading frame is expressed into E. coli as a specific double strand endonuclease. Cell. 1986 Feb 28;44(4):521–533. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90262-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper A. A., Stevens T. H. Protein splicing: self-splicing of genetically mobile elements at the protein level. Trends Biochem Sci. 1995 Sep;20(9):351–356. doi: 10.1016/s0968-0004(00)89075-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De La Salle H., Jacq C., Slonimski P. P. Critical sequences within mitochondrial introns: pleiotropic mRNA maturase and cis-dominant signals of the box intron controlling reductase and oxidase. Cell. 1982 Apr;28(4):721–732. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90051-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delahodde A., Goguel V., Becam A. M., Creusot F., Perea J., Banroques J., Jacq C. Site-specific DNA endonuclease and RNA maturase activities of two homologous intron-encoded proteins from yeast mitochondria. Cell. 1989 Feb 10;56(3):431–441. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90246-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dujardin G., Jacq C., Slonimski P. P. Single base substitution in an intron of oxidase gene compensates splicing defects of the cytochrome b gene. Nature. 1982 Aug 12;298(5875):628–632. doi: 10.1038/298628a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dujon B. Group I introns as mobile genetic elements: facts and mechanistic speculations--a review. Gene. 1989 Oct 15;82(1):91–114. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(89)90034-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dujon B., Slonimski P. P., Weill L. Mitochondrial genetics IX: A model for recombination and segregation of mitochondrial genomes in saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics. 1974 Sep;78(1):415–437. doi: 10.1093/genetics/78.1.415. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gimble F. S., Stephens B. W. Substitutions in conserved dodecapeptide motifs that uncouple the DNA binding and DNA cleavage activities of PI-SceI endonuclease. J Biol Chem. 1995 Mar 17;270(11):5849–5856. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.11.5849. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goguel V., Delahodde A., Jacq C. Connections between RNA splicing and DNA intron mobility in yeast mitochondria: RNA maturase and DNA endonuclease switching experiments. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Feb;12(2):696–705. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.2.696. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Golik P., Szczepanek T., Bartnik E., Stepien P. P., Lazowska J. The S. cerevisiae nuclear gene SUV3 encoding a putative RNA helicase is necessary for the stability of mitochondrial transcripts containing multiple introns. Curr Genet. 1995 Aug;28(3):217–224. doi: 10.1007/BF00309780. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groudinsky O., Dujardin G., Slonimski P. P. Long range control circuits within mitochondria and between nucleus and mitochondria. II. Genetic and biochemical analyses of suppressors which selectively alleviate the mitochondrial intron mutations. Mol Gen Genet. 1981;184(3):493–503. doi: 10.1007/BF00352529. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henke R. M., Butow R. A., Perlman P. S. Maturase and endonuclease functions depend on separate conserved domains of the bifunctional protein encoded by the group I intron aI4 alpha of yeast mitochondrial DNA. EMBO J. 1995 Oct 16;14(20):5094–5099. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1995.tb00191.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hensgens L. A., Bonen L., de Haan M., van der Horst G., Grivell L. A. Two intron sequences in yeast mitochondrial COX1 gene: homology among URF-containing introns and strain-dependent variation in flanking exons. Cell. 1983 Feb;32(2):379–389. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90457-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hodges R. A., Perler F. B., Noren C. J., Jack W. E. Protein splicing removes intervening sequences in an archaea DNA polymerase. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Dec 11;20(23):6153–6157. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.23.6153. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hudspeth M. E., Shumard D. S., Tatti K. M., Grossman L. I. Rapid purification of yeast mitochondrial DNA in high yield. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Dec 11;610(2):221–228. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(80)90003-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacquier A., Dujon B. An intron-encoded protein is active in a gene conversion process that spreads an intron into a mitochondrial gene. Cell. 1985 Jun;41(2):383–394. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80011-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labouesse M., Herbert C. J., Dujardin G., Slonimski P. P. Three suppressor mutations which cure a mitochondrial RNA maturase deficiency occur at the same codon in the open reading frame of the nuclear NAM2 gene. EMBO J. 1987 Mar;6(3):713–721. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04812.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labouesse M., Netter P., Schroeder R. Molecular basis of the 'box effect', A maturase deficiency leading to the absence of splicing of two introns located in two split genes of yeast mitochondrial DNA. Eur J Biochem. 1984 Oct 1;144(1):85–93. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb08434.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamb M. R., Anziano P. Q., Glaus K. R., Hanson D. K., Klapper H. J., Perlman P. S., Mahler H. R. Functional domains in introns. RNA processing intermediates in cis- and trans-acting mutants in the penultimate intron of the mitochondrial gene for cytochrome b. J Biol Chem. 1983 Feb 10;258(3):1991–1999. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambowitz A. M., Belfort M. Introns as mobile genetic elements. Annu Rev Biochem. 1993;62:587–622. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.62.070193.003103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazowska J., Claisse M., Gargouri A., Kotylak Z., Spyridakis A., Slonimski P. P. Protein encoded by the third intron of cytochrome b gene in Saccharomyces cerevisiae is an mRNA maturase. Analysis of mitochondrial mutants, RNA transcripts proteins and evolutionary relationships. J Mol Biol. 1989 Jan 20;205(2):275–289. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90341-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazowska J., Jacq C., Slonimski P. P. Sequence of introns and flanking exons in wild-type and box3 mutants of cytochrome b reveals an interlaced splicing protein coded by an intron. Cell. 1980 Nov;22(2 Pt 2):333–348. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90344-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazowska J., Meunier B., Macadre C. Homing of a group II intron in yeast mitochondrial DNA is accompanied by unidirectional co-conversion of upstream-located markers. EMBO J. 1994 Oct 17;13(20):4963–4972. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06823.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
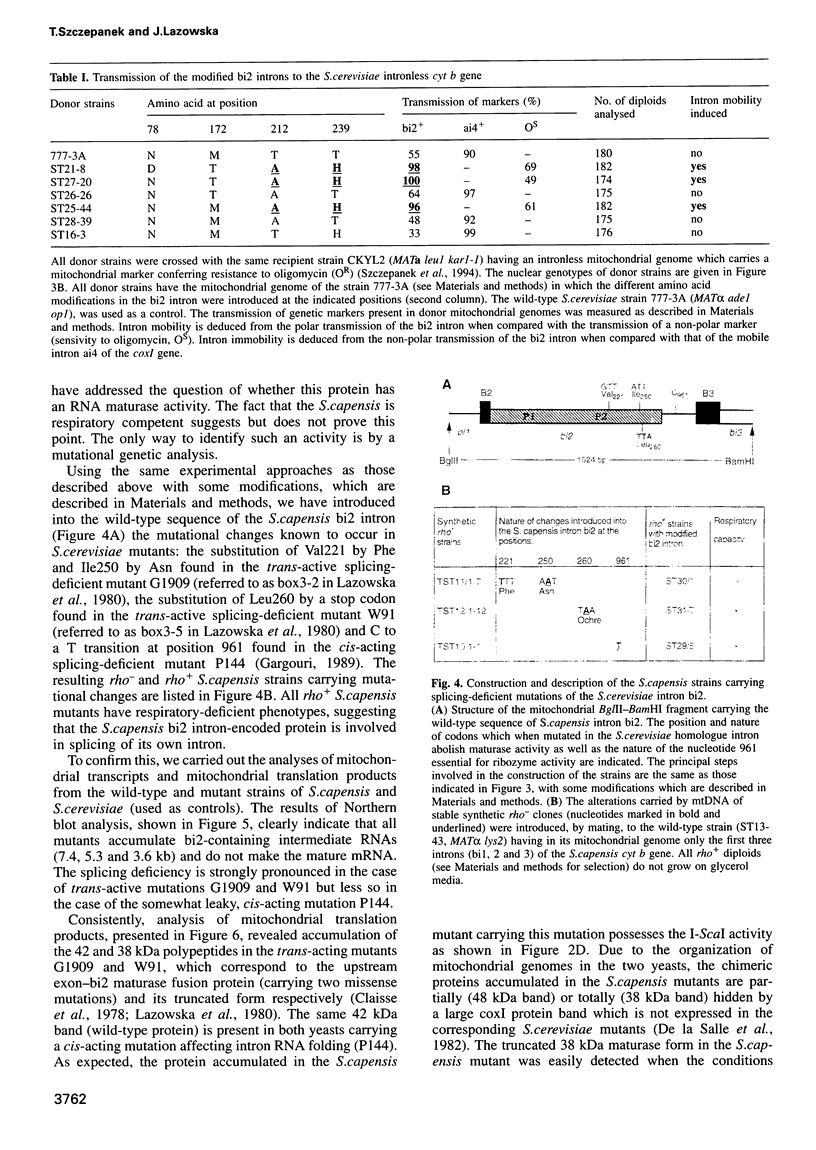
- Lazowska J., Szczepanek T., Macadre C., Dokova M. Two homologous mitochondrial introns from closely related Saccharomyces species differ by only a few amino acid replacements in their Open Reading Frames: one is mobile, the other is not. C R Acad Sci III. 1992;315(2):37–41. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macreadie I. G., Scott R. M., Zinn A. R., Butow R. A. Transposition of an intron in yeast mitochondria requires a protein encoded by that intron. Cell. 1985 Jun;41(2):395–402. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80012-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michel F., Jacquier A., Dujon B. Comparison of fungal mitochondrial introns reveals extensive homologies in RNA secondary structure. Biochimie. 1982 Oct;64(10):867–881. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(82)80349-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moran J. V., Wernette C. M., Mecklenburg K. L., Butow R. A., Perlman P. S. Intron 5 alpha of the COXI gene of yeast mitochondrial DNA is a mobile group I intron. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Aug 11;20(15):4069–4076. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.15.4069. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulero J. J., Fox T. D. Alteration of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae COX2 mRNA 5'-untranslated leader by mitochondrial gene replacement and functional interaction with the translational activator protein PET111. Mol Biol Cell. 1993 Dec;4(12):1327–1335. doi: 10.1091/mbc.4.12.1327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perrin A., Buckle M., Dujon B. Asymmetrical recognition and activity of the I-SceI endonuclease on its site and on intron-exon junctions. EMBO J. 1993 Jul;12(7):2939–2947. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05956.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sargueil B., Delahodde A., Hatat D., Tian G. L., Lazowska J., Jacq C. A new specific DNA endonuclease activity in yeast mitochondria. Mol Gen Genet. 1991 Feb;225(2):340–341. doi: 10.1007/BF00269867. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sargueil B., Hatat D., Delahodde A., Jacq C. In vivo and in vitro analyses of an intron-encoded DNA endonuclease from yeast mitochondria. Recognition site by site-directed mutagenesis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Oct 11;18(19):5659–5665. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.19.5659. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schapira M., Desdouets C., Jacq C., Perea J. I-Sce III an intron-encoded DNA endonuclease from yeast mitochondria. Asymmetrical DNA binding properties and cleavage reaction. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Aug 11;21(16):3683–3689. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.16.3683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szczepanek T., Macadre C., Meunier B., Lazowska J. Two homologous introns from related Saccharomyces species differ in their mobility. Gene. 1994 Feb 11;139(1):1–7. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(94)90516-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szostak J. W., Orr-Weaver T. L., Rothstein R. J., Stahl F. W. The double-strand-break repair model for recombination. Cell. 1983 May;33(1):25–35. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90331-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Séraphin B., Faye G., Hatat D., Jacq C. The yeast mitochondrial intron aI5 alpha: associated endonuclease activity and in vivo mobility. Gene. 1992 Apr 1;113(1):1–8. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(92)90663-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tian G. L., Michel F., Macadre C., Slonimski P. P., Lazowska J. Incipient mitochondrial evolution in yeasts. II. The complete sequence of the gene coding for cytochrome b in Saccharomyces douglasii reveals the presence of both new and conserved introns and discloses major differences in the fixation of mutations in evolution. J Mol Biol. 1991 Apr 20;218(4):747–760. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(91)90263-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waring R. B., Davies R. W., Scazzocchio C., Brown T. A. Internal structure of a mitochondrial intron of Aspergillus nidulans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Oct;79(20):6332–6336. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.20.6332. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss-Brummer B., Rödel G., Schweyen R. J., Kaudewitz F. Expression of the split gene cob in yeast: evidence for a precursor of a "maturase" protein translated from intron 4 and preceding exons. Cell. 1982 Jun;29(2):527–536. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90169-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wenzlau J. M., Saldanha R. J., Butow R. A., Perlman P. S. A latent intron-encoded maturase is also an endonuclease needed for intron mobility. Cell. 1989 Feb 10;56(3):421–430. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90245-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- di Rago J. P., Netter P., Slonimski P. P. Pseudo-wild type revertants from inactive apocytochrome b mutants as a tool for the analysis of the structure/function relationships of the mitochondrial ubiquinol-cytochrome c reductase of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biol Chem. 1990 Feb 25;265(6):3332–3339. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]