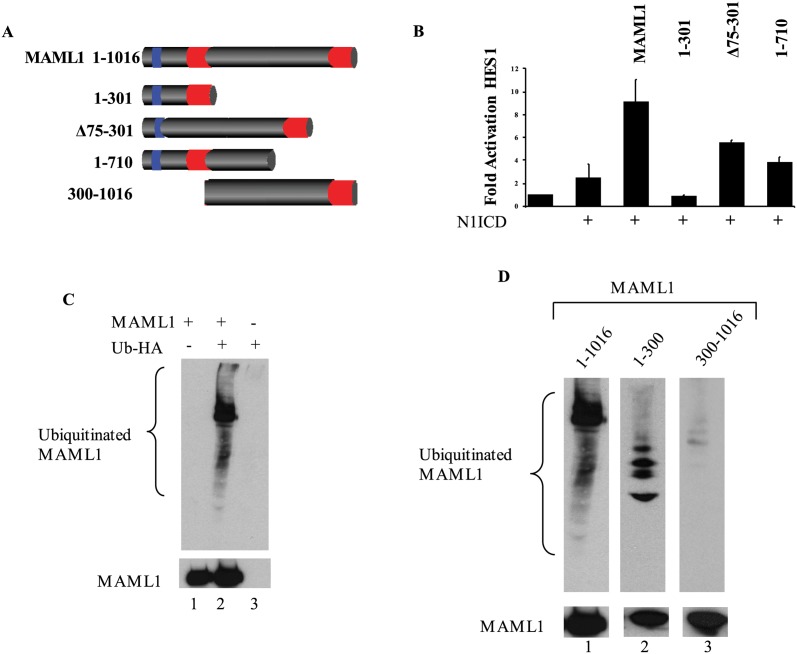
Fig 2. MAML1 is Ubiquitinated.
(A) Cartoon depiction of MAML1 and the deletion constructs used in this study. MAML1 has been shown to have three domains, two acidic domains as indicated by red and one basic domain as indicated by blue. The acidic domain at the N-terminus (1–75 aa) has been shown to interact with the N1ICD. The central basic domain (75–300 aa) has been shown to interact with p300. The c-terminus domain has not been shown to interact with any proteins. (B) HES1 is activated by a combination of N1ICD with MAML1. Deletion of various domains of MAML1 show decreased reporter activity. Results are normalized to renilla luciferase and fold activation is compared to HES1 alone (n = 3). (C) MAML1 is ubiquitinated. MAML1 was overexpressed with HA-Ub. MAML1 was immunoprecipitated and western blots were performed to HA (Top blot) or MAML1 (lower blot) to show expression levels. (D) Ubiquitination of MAML1 occurs in the first 300 amino acids. MAML1 full-length, MAML1-1-300 or MAML1-300-1016 were expressed with HA-Ub and immunoprecipitated. Western blots were performed to ubiquitin (HA, top blot) or MAML1 constructs (Myc, bottom blot).