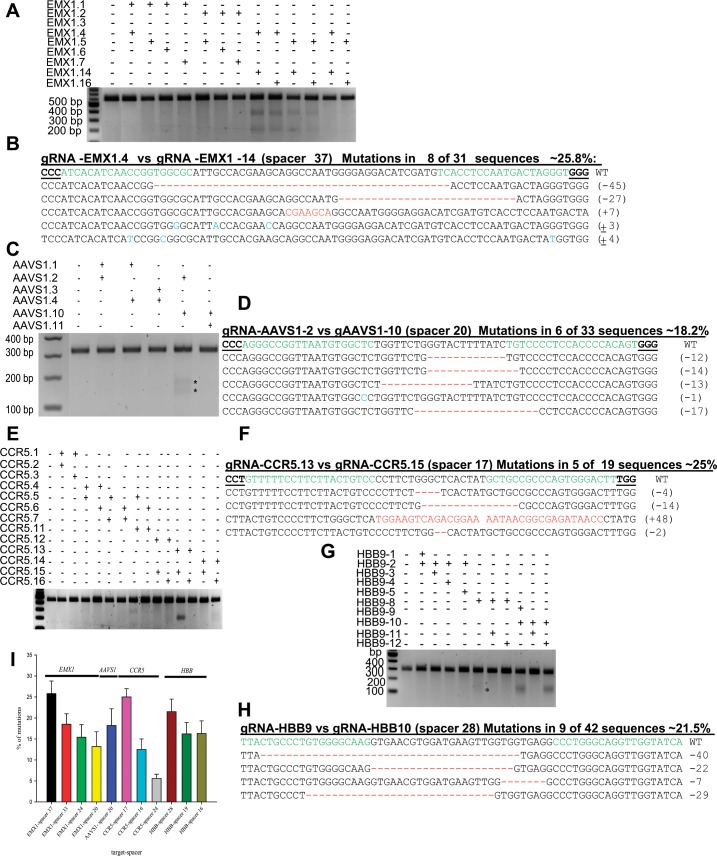
Fig 3. Robust catalytic activity of the fdCas9 variant on endogenous genomic targets.
(A, C, E, and G) T7EI assays for the EMX1, AAVS1, CCR5, and HBB genomic targets, respectively with fdCas9 using several combinations of gRNAs in PAM-in and PAM-out orientations. Arrows in (C) indicate the expected size of the DNA bands of AAVS1 amplicons cleaved by T7EI. (B, D, F, and H) Alignment of Sanger sequencing reads of PCR amplicons encompassing the EMX1, AAVS1, CCR5, and HBB target sequences showing indels within the 37-, 20-, 17-, and 28-bp spacer sequences, respectively. gRNA targets are highlighted in green, the PAM sequence is shown in bold and underlined, dashes indicate nucleotide deletions, nucleotides highlighted in red indicate insertions, and nucleotides highlighted in blue indicate substitutions. Mutation frequencies were estimated as the number of mutant clones divided by the total number of sequenced clones. (I) Catalytic activities of fdCas9 on different genomic targets using gRNA pairs with different spacer sizes (represented in percentage).