Figure 1.
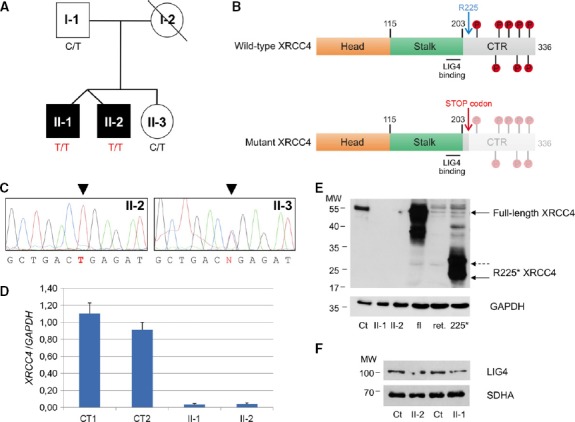
- Pedigree. Black symbols designate affected subjects.
- Schematic view of wild-type and mutant (R225*) XRCC4 proteins with their main domains and phosphorylation sites. The numbering refers to amino acids of refseq: NP_071801.1. CTR: C-terminal region.
- Electropherograms of the XRCC4 genomic region encompassing the nucleotide substitutions in available members of the family.
- Quantitative real-time PCR of XRCC4 relative to GAPDH mRNA in affected (II-1 and II-2) and control (CT1 and CT2) fibroblasts. Each value refers to the mean of three independent experiments performed in duplicate. Error bars indicate the standard deviation.
- Immunoblot analysis of total lysates from fibroblasts (fbs) and of in vitro-synthesized proteins (i.v.p). fl: in vitro-translated full-length XRCC4 protein; ret.: reticulocyte lysate used for in vitro protein synthesis; 225*: in vitro-translated XRCC4 R225* truncated protein; Ct: lysate of control fbs; and II-1 and II-2: lysates of fbs from patient II-1 and II-2. α-XRCC4 (Abcam, 1:1,000) and α-GAPDH antibodies were used.
- Immunoblot analysis of total lysates from fibroblasts using α-LIG4 (GeneTex, 1:1,000) and α-SDHA antibodies. Ct: lysate of control fbs; II-1 and II-2: lysates of fbs from patient II-1 and II-2. The position of the molecular weight (MW) marker proteins is indicated.
