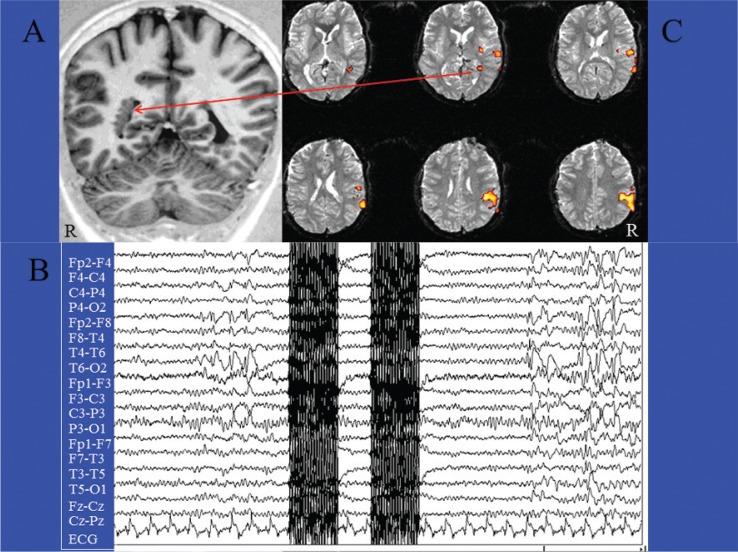
Figure 1.
The classical spike-triggered method in a case of focal epilepsy.
Patient (female, 23 yrs) with focal epilepsy and multiple nodules of subependymal heterotopia, mainly in the right hemisphere (A). EEG-fMRI acquisition of two EPI scans triggered by interictal epileptic activities (spikes and waves) recorded on the scalp, mainly from the T4-T6-P4 electrodes (B). After acquiring an equal number of EPI scans without spikes for at least 25”, the interictal and basal images were statistically compared by t-test analysis (statistical parametric mapping). The fMRI map disclosed right temporoparietal areas of BOLD decrease, including a deep cluster located within one of the subependymal nodules (C).