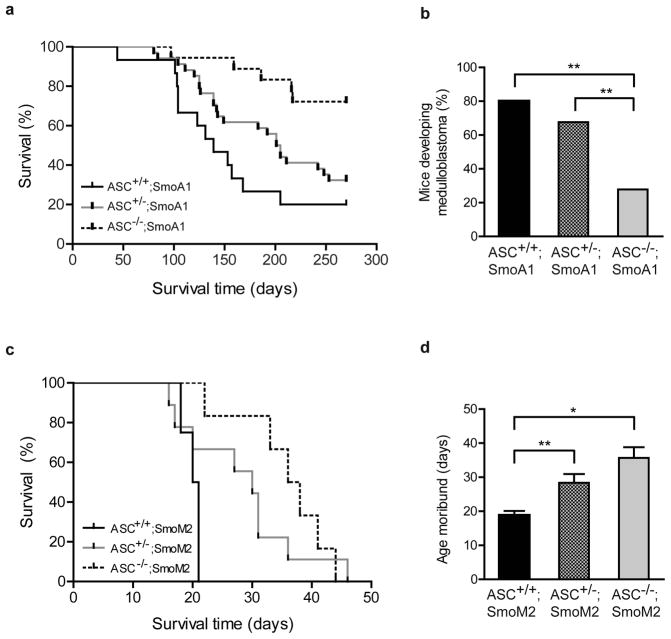
Figure 2.
ASC deficiency suppresses medulloblastoma tumorigenesis in the SmoA1 and SmoM2 mouse models. (a) Kaplan-Meier analysis of ASC+/+;SmoA1 mice (n=15), ASC+/−;SmoA1 mice (n=34), and ASC−/−;SmoA1 mice (n=18) reveals a significant difference in tumor incidence with ASC expression (P=0.0019; Log-Rank test). ASC deficiency significantly decreased tumor frequency and increased tumor latency when compared to ASC+/+;SmoA1 (P=0.0004; Log-Rank test) and ASC+/−;SmoA1 mice (P=0.0077; Log-Rank test). (P=0.1108 between ASC+/−;SmoA1 and ASC+/+;SmoA1 mice; Log-Rank test.) (b) Overall incidence of medulloblastoma by P270 is reduced in ASC−/−;SmoA1 versus ASC+/+;SmoA1 (P=0.0049; Fisher’s exact test) and ASC+/−;SmoA1 (P=0.0088; Fisher’s exact test) mice; **P<0.01. (c) Kaplan-Meier analysis of ASC+/+;SmoM2 mice (n=4), ASC+/−;SmoM2 mice (n=9), and ASC−/−;SmoM2 mice (n=6) reveals a significant difference in tumorigenesis with ASC expression (P= 0.0004; Log-Rank test). ASC+/+;SmoM2 mice displayed shorter tumor latency than either ASC−/−;SmoM2 (P=0.0025; Log-Rank test) or ASC+/−;SmoM2 (P=0.0003; Log-Rank test) mice. (P=0.732 between ASC+/−;SmoM2 and ASC−/−;SmoM2 mice; Log-Rank test.) (d) The average age mice become moribund is increased with ASC deficiency in ASC−/−;SmoM2 mice and ASC+/−;SmoM2 mice. **P=0.004; *P=0.025 (Student’s t-test).