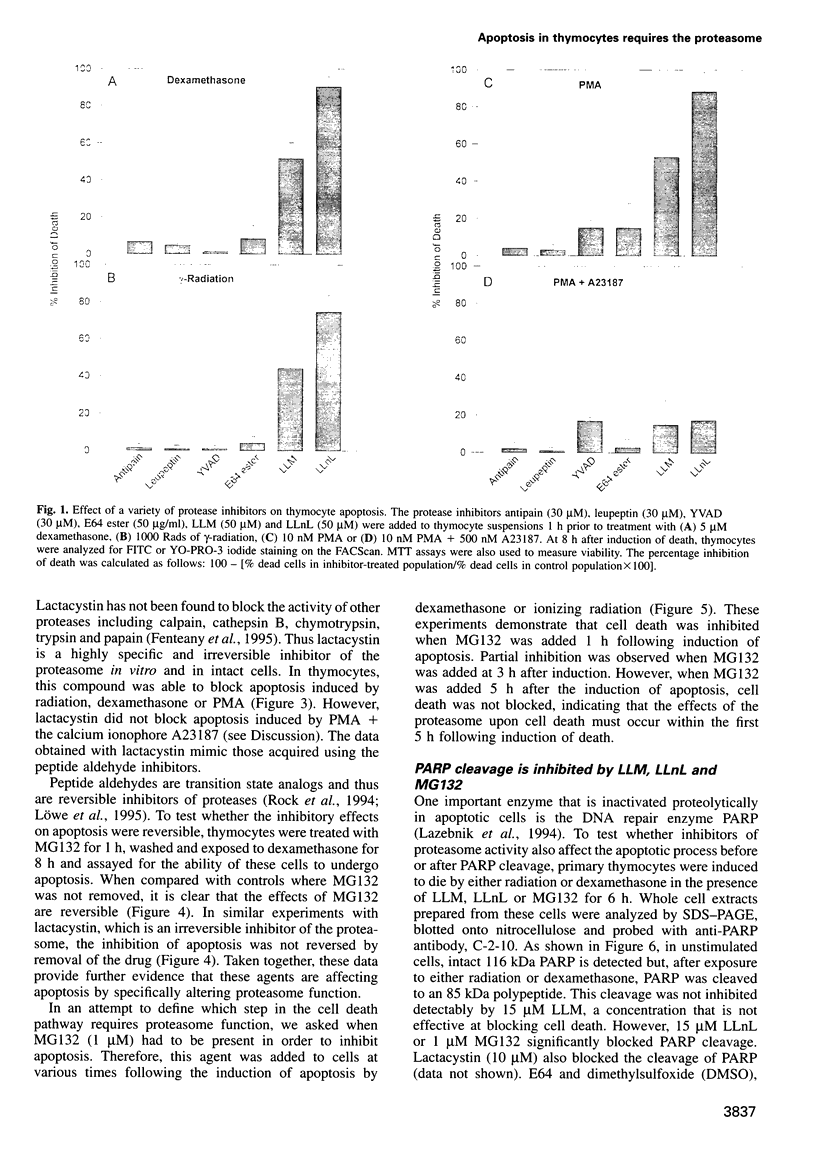
Abstract
Cell death in many different organisms requires the activation of proteolytic cascades involving cytosolic proteases. Here we describe a novel requirement in thymocyte cell death for the 20S proteasome, a highly conserved multicatalytic protease found in all eukaryotes. Specific inhibitors of proteasome function blocked cell death induced by ionizing radiation, glucocorticoids or phorbol ester. In addition to inhibiting apoptosis, these signals prevented the cleavage of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase that accompanies many cell deaths. Since overall rates of protein degradation were not altered significantly during cell death in thymocytes, these results suggest that the proteasome may either degrade regulatory protein(s) that normally inhibit the apoptotic pathway or may proteolytically activate protein(s) than promote cell death.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Calnan B. J., Szychowski S., Chan F. K., Cado D., Winoto A. A role for the orphan steroid receptor Nur77 in apoptosis accompanying antigen-induced negative selection. Immunity. 1995 Sep;3(3):273–282. doi: 10.1016/1074-7613(95)90113-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casciola-Rosen L. A., Miller D. K., Anhalt G. J., Rosen A. Specific cleavage of the 70-kDa protein component of the U1 small nuclear ribonucleoprotein is a characteristic biochemical feature of apoptotic cell death. J Biol Chem. 1994 Dec 9;269(49):30757–30760. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen Z., Hagler J., Palombella V. J., Melandri F., Scherer D., Ballard D., Maniatis T. Signal-induced site-specific phosphorylation targets I kappa B alpha to the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway. Genes Dev. 1995 Jul 1;9(13):1586–1597. doi: 10.1101/gad.9.13.1586. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke A. R., Purdie C. A., Harrison D. J., Morris R. G., Bird C. C., Hooper M. L., Wyllie A. H. Thymocyte apoptosis induced by p53-dependent and independent pathways. Nature. 1993 Apr 29;362(6423):849–852. doi: 10.1038/362849a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dawson S. P., Arnold J. E., Mayer N. J., Reynolds S. E., Billett M. A., Gordon C., Colleaux L., Kloetzel P. M., Tanaka K., Mayer R. J. Developmental changes of the 26 S proteasome in abdominal intersegmental muscles of Manduca sexta during programmed cell death. J Biol Chem. 1995 Jan 27;270(4):1850–1858. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.4.1850. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dieken E. S., Miesfeld R. L. Transcriptional transactivation functions localized to the glucocorticoid receptor N terminus are necessary for steroid induction of lymphocyte apoptosis. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Feb;12(2):589–597. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.2.589. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Driscoll J., Brown M. G., Finley D., Monaco J. J. MHC-linked LMP gene products specifically alter peptidase activities of the proteasome. Nature. 1993 Sep 16;365(6443):262–264. doi: 10.1038/365262a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faucheu C., Diu A., Chan A. W., Blanchet A. M., Miossec C., Hervé F., Collard-Dutilleul V., Gu Y., Aldape R. A., Lippke J. A. A novel human protease similar to the interleukin-1 beta converting enzyme induces apoptosis in transfected cells. EMBO J. 1995 May 1;14(9):1914–1922. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1995.tb07183.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fenteany G., Standaert R. F., Lane W. S., Choi S., Corey E. J., Schreiber S. L. Inhibition of proteasome activities and subunit-specific amino-terminal threonine modification by lactacystin. Science. 1995 May 5;268(5211):726–731. doi: 10.1126/science.7732382. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernandes-Alnemri T., Litwack G., Alnemri E. S. CPP32, a novel human apoptotic protein with homology to Caenorhabditis elegans cell death protein Ced-3 and mammalian interleukin-1 beta-converting enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1994 Dec 9;269(49):30761–30764. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernandes-Alnemri T., Litwack G., Alnemri E. S. Mch2, a new member of the apoptotic Ced-3/Ice cysteine protease gene family. Cancer Res. 1995 Jul 1;55(13):2737–2742. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaczynska M., Rock K. L., Goldberg A. L. Gamma-interferon and expression of MHC genes regulate peptide hydrolysis by proteasomes. Nature. 1993 Sep 16;365(6443):264–267. doi: 10.1038/365264a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glotzer M., Murray A. W., Kirschner M. W. Cyclin is degraded by the ubiquitin pathway. Nature. 1991 Jan 10;349(6305):132–138. doi: 10.1038/349132a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg A. L., Stein R., Adams J. New insights into proteasome function: from archaebacteria to drug development. Chem Biol. 1995 Aug;2(8):503–508. doi: 10.1016/1074-5521(95)90182-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imajoh-Ohmi S., Kawaguchi T., Sugiyama S., Tanaka K., Omura S., Kikuchi H. Lactacystin, a specific inhibitor of the proteasome, induces apoptosis in human monoblast U937 cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1995 Dec 26;217(3):1070–1077. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1995.2878. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones M. E., Haire M. F., Kloetzel P. M., Mykles D. L., Schwartz L. M. Changes in the structure and function of the multicatalytic proteinase (proteasome) during programmed cell death in the intersegmental muscles of the hawkmoth, Manduca sexta. Dev Biol. 1995 Jun;169(2):436–447. doi: 10.1006/dbio.1995.1159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufmann S. H., Desnoyers S., Ottaviano Y., Davidson N. E., Poirier G. G. Specific proteolytic cleavage of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase: an early marker of chemotherapy-induced apoptosis. Cancer Res. 1993 Sep 1;53(17):3976–3985. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumar S., Kinoshita M., Noda M., Copeland N. G., Jenkins N. A. Induction of apoptosis by the mouse Nedd2 gene, which encodes a protein similar to the product of the Caenorhabditis elegans cell death gene ced-3 and the mammalian IL-1 beta-converting enzyme. Genes Dev. 1994 Jul 15;8(14):1613–1626. doi: 10.1101/gad.8.14.1613. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamarre D., Talbot B., Leduc Y., Muller S., Poirier G. Production and characterization of monoclonal antibodies specific for the functional domains of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase. Biochem Cell Biol. 1986 Apr;64(4):368–376. doi: 10.1139/o86-051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazebnik Y. A., Kaufmann S. H., Desnoyers S., Poirier G. G., Earnshaw W. C. Cleavage of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase by a proteinase with properties like ICE. Nature. 1994 Sep 22;371(6495):346–347. doi: 10.1038/371346a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin K. I., Lee S. H., Narayanan R., Baraban J. M., Hardwick J. M., Ratan R. R. Thiol agents and Bcl-2 identify an alphavirus-induced apoptotic pathway that requires activation of the transcription factor NF-kappa B. J Cell Biol. 1995 Dec;131(5):1149–1161. doi: 10.1083/jcb.131.5.1149. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu Z. G., Smith S. W., McLaughlin K. A., Schwartz L. M., Osborne B. A. Apoptotic signals delivered through the T-cell receptor of a T-cell hybrid require the immediate-early gene nur77. Nature. 1994 Jan 20;367(6460):281–284. doi: 10.1038/367281a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowe S. W., Schmitt E. M., Smith S. W., Osborne B. A., Jacks T. p53 is required for radiation-induced apoptosis in mouse thymocytes. Nature. 1993 Apr 29;362(6423):847–849. doi: 10.1038/362847a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Löwe J., Stock D., Jap B., Zwickl P., Baumeister W., Huber R. Crystal structure of the 20S proteasome from the archaeon T. acidophilum at 3.4 A resolution. Science. 1995 Apr 28;268(5210):533–539. doi: 10.1126/science.7725097. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin S. J., Green D. R. Protease activation during apoptosis: death by a thousand cuts? Cell. 1995 Aug 11;82(3):349–352. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90422-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin S. J., O'Brien G. A., Nishioka W. K., McGahon A. J., Mahboubi A., Saido T. C., Green D. R. Proteolysis of fodrin (non-erythroid spectrin) during apoptosis. J Biol Chem. 1995 Mar 24;270(12):6425–6428. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.12.6425. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Medina R., Wing S. S., Goldberg A. L. Increase in levels of polyubiquitin and proteasome mRNA in skeletal muscle during starvation and denervation atrophy. Biochem J. 1995 May 1;307(Pt 3):631–637. doi: 10.1042/bj3070631. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milligan C. E., Prevette D., Yaginuma H., Homma S., Cardwell C., Fritz L. C., Tomaselli K. J., Oppenheim R. W., Schwartz L. M. Peptide inhibitors of the ICE protease family arrest programmed cell death of motoneurons in vivo and in vitro. Neuron. 1995 Aug;15(2):385–393. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(95)90042-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miura M., Zhu H., Rotello R., Hartwieg E. A., Yuan J. Induction of apoptosis in fibroblasts by IL-1 beta-converting enzyme, a mammalian homolog of the C. elegans cell death gene ced-3. Cell. 1993 Nov 19;75(4):653–660. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90486-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neamati N., Fernandez A., Wright S., Kiefer J., McConkey D. J. Degradation of lamin B1 precedes oligonucleosomal DNA fragmentation in apoptotic thymocytes and isolated thymocyte nuclei. J Immunol. 1995 Apr 15;154(8):3788–3795. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholson D. W., Ali A., Thornberry N. A., Vaillancourt J. P., Ding C. K., Gallant M., Gareau Y., Griffin P. R., Labelle M., Lazebnik Y. A. Identification and inhibition of the ICE/CED-3 protease necessary for mammalian apoptosis. Nature. 1995 Jul 6;376(6535):37–43. doi: 10.1038/376037a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborne B. A., Smith S. W., Liu Z. G., McLaughlin K. A., Grimm L., Schwartz L. M. Identification of genes induced during apoptosis in T lymphocytes. Immunol Rev. 1994 Dec;142:301–320. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1994.tb00894.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pagano M., Tam S. W., Theodoras A. M., Beer-Romero P., Del Sal G., Chau V., Yew P. R., Draetta G. F., Rolfe M. Role of the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway in regulating abundance of the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p27. Science. 1995 Aug 4;269(5224):682–685. doi: 10.1126/science.7624798. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palombella V. J., Rando O. J., Goldberg A. L., Maniatis T. The ubiquitin-proteasome pathway is required for processing the NF-kappa B1 precursor protein and the activation of NF-kappa B. Cell. 1994 Sep 9;78(5):773–785. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(94)90482-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raff M. C., Barres B. A., Burne J. F., Coles H. S., Ishizaki Y., Jacobson M. D. Programmed cell death and the control of cell survival: lessons from the nervous system. Science. 1993 Oct 29;262(5134):695–700. doi: 10.1126/science.8235590. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
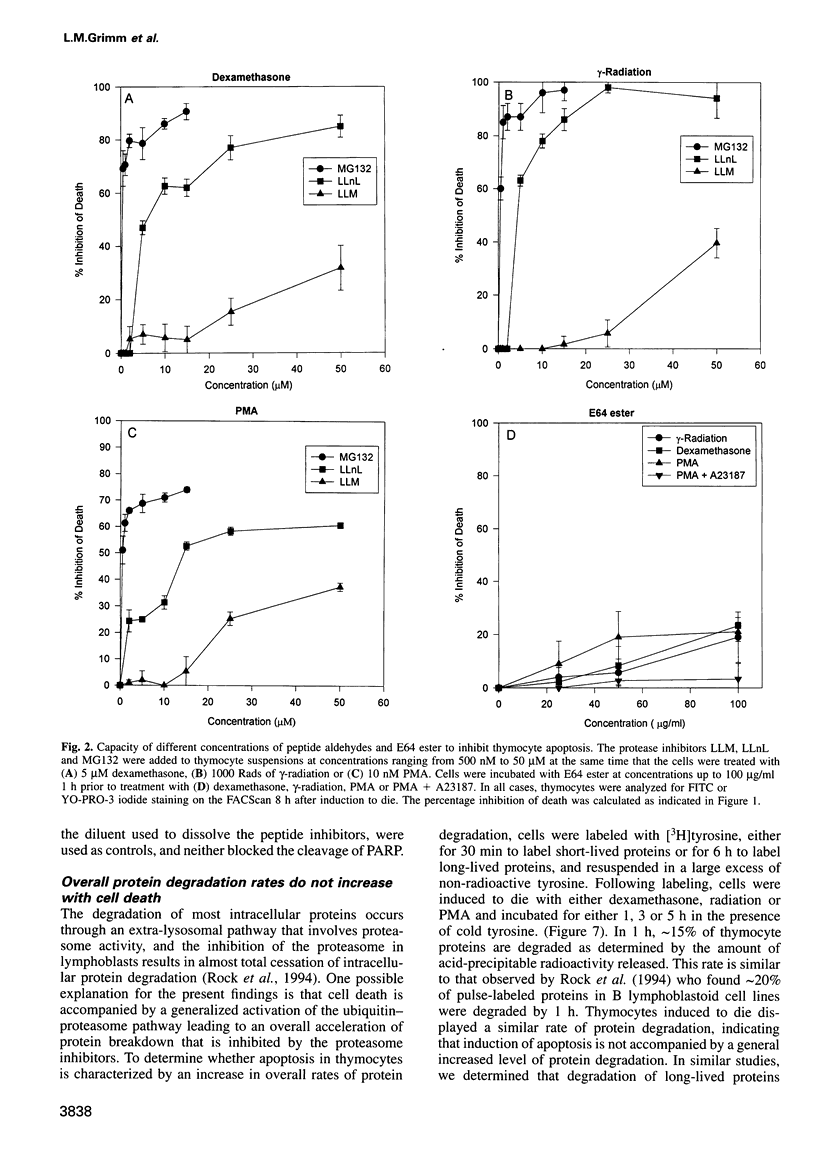
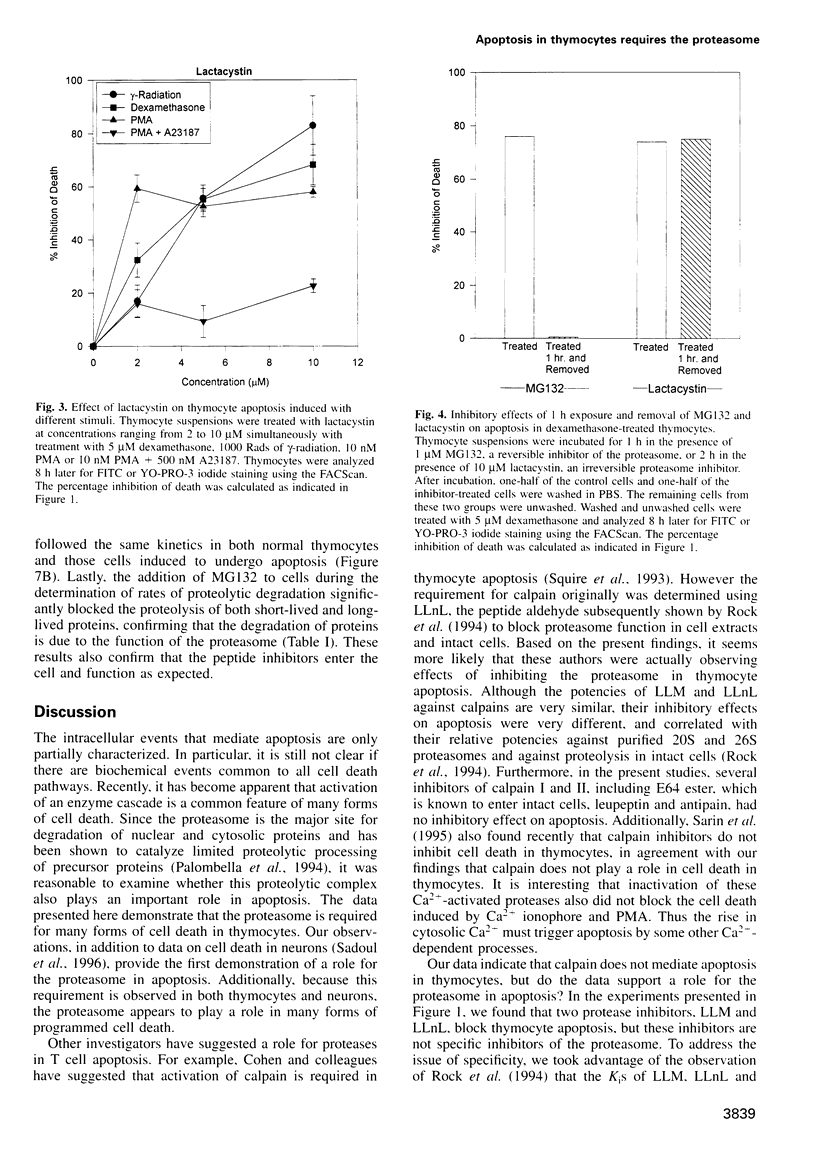
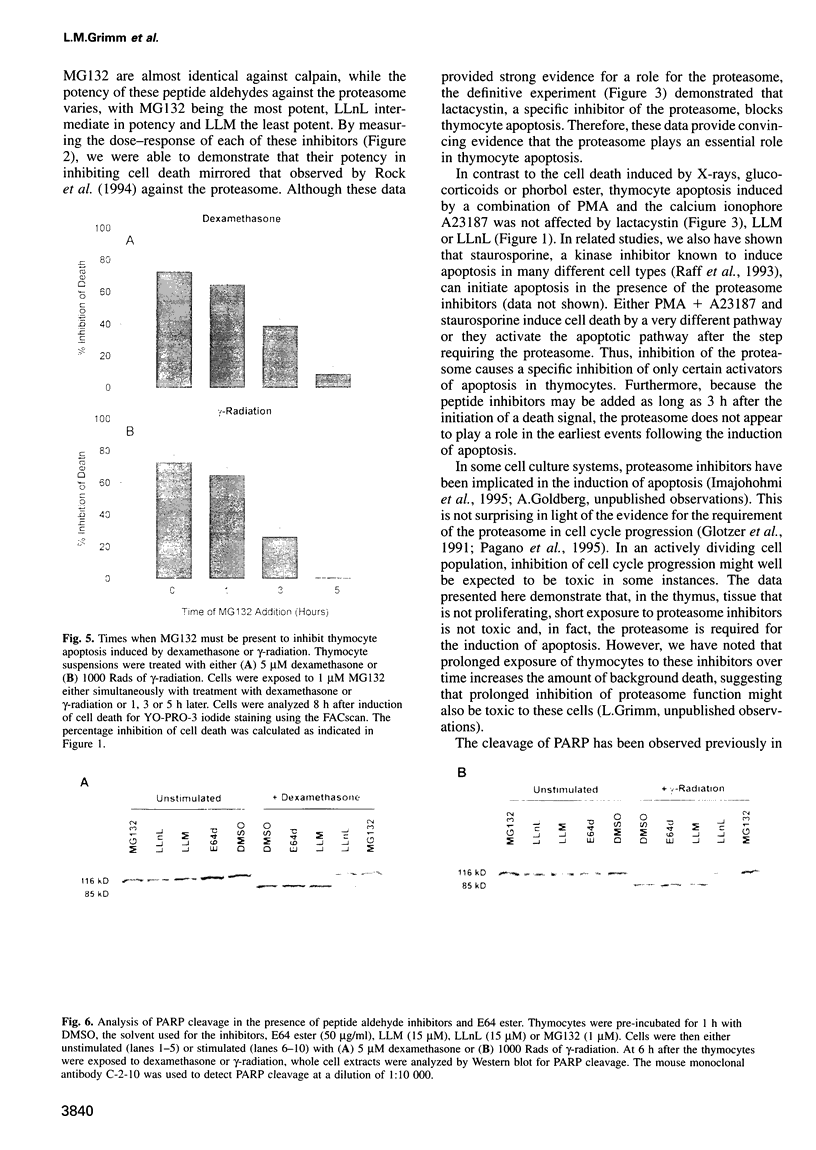
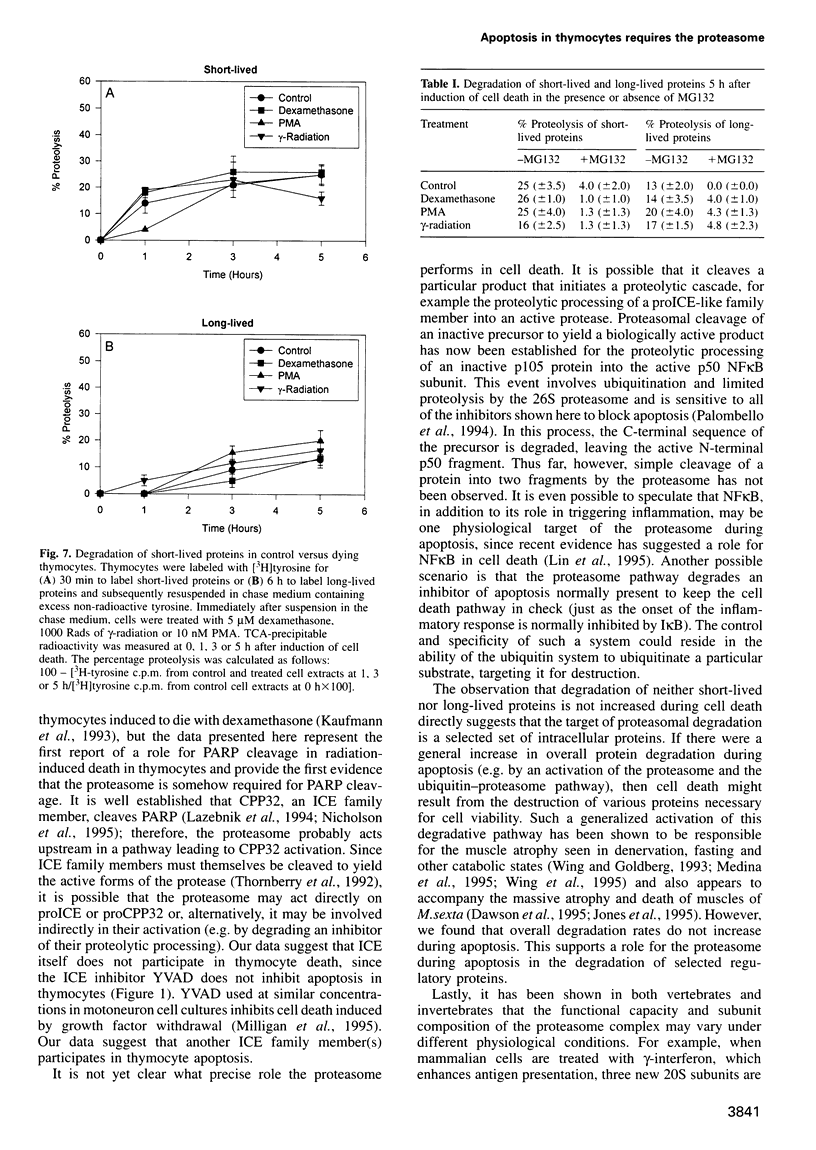
- Rock K. L., Gramm C., Rothstein L., Clark K., Stein R., Dick L., Hwang D., Goldberg A. L. Inhibitors of the proteasome block the degradation of most cell proteins and the generation of peptides presented on MHC class I molecules. Cell. 1994 Sep 9;78(5):761–771. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(94)90462-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadoul R., Fernandez P. A., Quiquerez A. L., Martinou I., Maki M., Schröter M., Becherer J. D., Irmler M., Tschopp J., Martinou J. C. Involvement of the proteasome in the programmed cell death of NGF-deprived sympathetic neurons. EMBO J. 1996 Aug 1;15(15):3845–3852. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarin A., Nakajima H., Henkart P. A. A protease-dependent TCR-induced death pathway in mature lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1995 Jun 1;154(11):5806–5812. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheffner M., Werness B. A., Huibregtse J. M., Levine A. J., Howley P. M. The E6 oncoprotein encoded by human papillomavirus types 16 and 18 promotes the degradation of p53. Cell. 1990 Dec 21;63(6):1129–1136. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90409-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seemüller E., Lupas A., Stock D., Löwe J., Huber R., Baumeister W. Proteasome from Thermoplasma acidophilum: a threonine protease. Science. 1995 Apr 28;268(5210):579–582. doi: 10.1126/science.7725107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Squìer M. K., Miller A. C., Malkinson A. M., Cohen J. J. Calpain activation in apoptosis. J Cell Physiol. 1994 May;159(2):229–237. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041590206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tewari M., Quan L. T., O'Rourke K., Desnoyers S., Zeng Z., Beidler D. R., Poirier G. G., Salvesen G. S., Dixit V. M. Yama/CPP32 beta, a mammalian homolog of CED-3, is a CrmA-inhibitable protease that cleaves the death substrate poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase. Cell. 1995 Jun 2;81(5):801–809. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90541-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thornberry N. A., Bull H. G., Calaycay J. R., Chapman K. T., Howard A. D., Kostura M. J., Miller D. K., Molineaux S. M., Weidner J. R., Aunins J. A novel heterodimeric cysteine protease is required for interleukin-1 beta processing in monocytes. Nature. 1992 Apr 30;356(6372):768–774. doi: 10.1038/356768a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang L., Miura M., Bergeron L., Zhu H., Yuan J. Ich-1, an Ice/ced-3-related gene, encodes both positive and negative regulators of programmed cell death. Cell. 1994 Sep 9;78(5):739–750. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(94)90422-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wefes I., Kaiser P., Schneider R., Pickart C. M., Finley D. Characterization of a cDNA clone encoding E2-20K, a murine ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme. Gene. 1995 Oct 3;163(2):321–322. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(95)00374-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson K. P., Black J. A., Thomson J. A., Kim E. E., Griffith J. P., Navia M. A., Murcko M. A., Chambers S. P., Aldape R. A., Raybuck S. A. Structure and mechanism of interleukin-1 beta converting enzyme. Nature. 1994 Jul 28;370(6487):270–275. doi: 10.1038/370270a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wing S. S., Goldberg A. L. Glucocorticoids activate the ATP-ubiquitin-dependent proteolytic system in skeletal muscle during fasting. Am J Physiol. 1993 Apr;264(4 Pt 1):E668–E676. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1993.264.4.E668. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wing S. S., Haas A. L., Goldberg A. L. Increase in ubiquitin-protein conjugates concomitant with the increase in proteolysis in rat skeletal muscle during starvation and atrophy denervation. Biochem J. 1995 May 1;307(Pt 3):639–645. doi: 10.1042/bj3070639. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woronicz J. D., Calnan B., Ngo V., Winoto A. Requirement for the orphan steroid receptor Nur77 in apoptosis of T-cell hybridomas. Nature. 1994 Jan 20;367(6460):277–281. doi: 10.1038/367277a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yuan J., Shaham S., Ledoux S., Ellis H. M., Horvitz H. R. The C. elegans cell death gene ced-3 encodes a protein similar to mammalian interleukin-1 beta-converting enzyme. Cell. 1993 Nov 19;75(4):641–652. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90485-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]