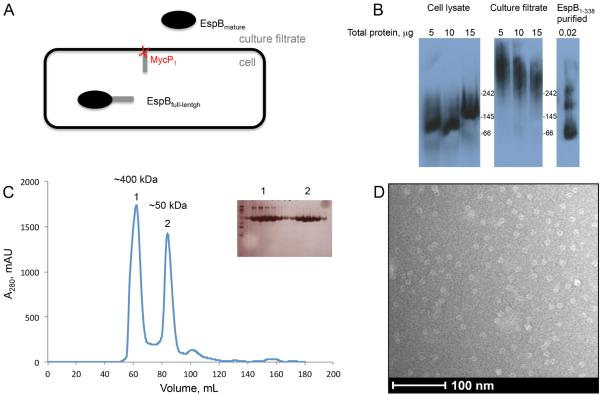
Fig. 1.
Oligomeric state of EspB.
A. EspB secretion model. The full-length protein (460 amino acids) is organized in two domains. The N-terminal domain belongs to the PE–PPE family and the C-terminal domain is predicted to be intrinsically disordered. The N-terminal fragment of EspB is secreted in the culture filtrate as the mature form after the cleavage by the serine protease MycP1 (McLaughlin et al., 2007; Xu et al., 2007; Ohol et al., 2010).
B. Immuno-blotting of a native gel with different concentrations of cell lysate, culture filtrate of M. tuberculosis and purified EspB1-338. Positions of molecular weight markers (kDa) are indicated.
C. Size exclusion chromatography profile of purified EspB1-338 in 20mM Tris pH 8.5, 150 mM NaCl. Insert shows an SDS-PAGE of the peak fractions. The approximate size of oligomers (1) and monomers (2) were calculated by linear extrapolation.
D. Electron microscopy image of negative-stained EspB1-338.