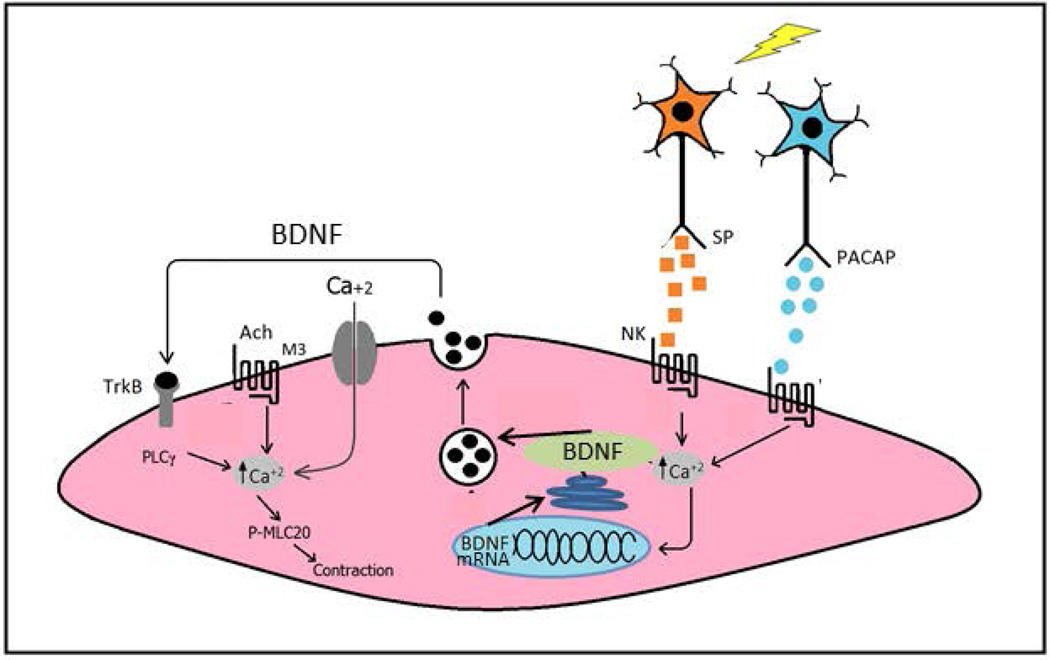
Figure 7.
Model of the expression and role of BDNF in intestinal longitudinal muscle. Based on the results of the present study and our recent study (2) of the effects of BDNF on longitudinal muscle of the rabbit we propose the model for the action of BDNF. Release of neurotransmitters pituitary adenylate cyclase-activating peptide (PACAP) and substance P (SP) from enteric neurons activates receptors on longitudinal smooth muscle cells to increase [Ca2+]i. The increase in [Ca2+]i causes increased transcription of the bdnf gene, increase in BDNF mRNA, and increase in BDNF protein expression and secretion. BDNF in turn acts in an autocrine manner to augment cholinergic muscarinic contraction of longitudinal muscle via activation of specific trk B receptors on longitudinal smooth muscle cells which is mediated by increased activation of PLC-γ (2).