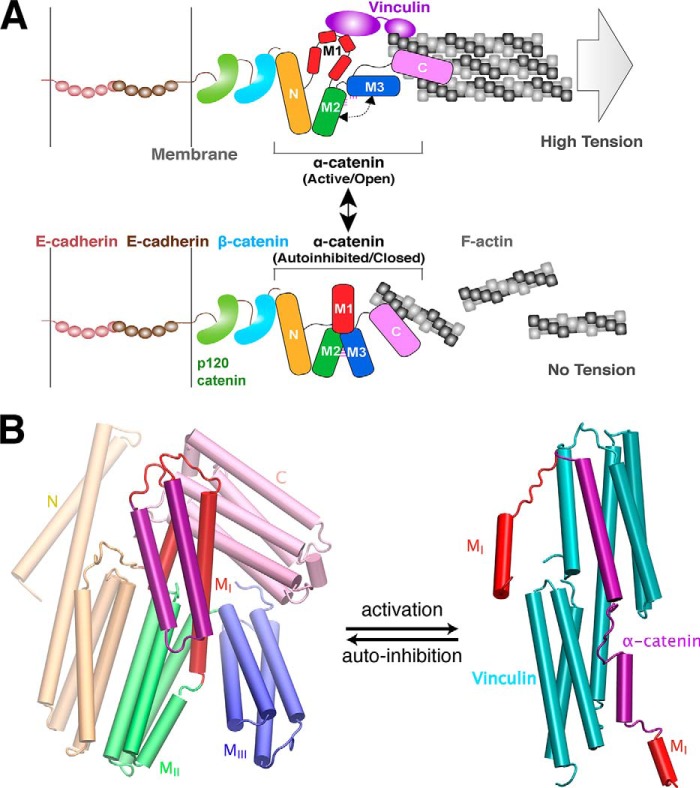
FIGURE 2.
Conformational switching model of α-catenin between two known functional states. A, model of α-catenin-dependent interactions between the cadherin-catenin complex and F-actin. As a multidomain protein, α-catenin physically links the cadherin-catenin complex to actin filaments (F-actin) through the N-terminal β-catenin-binding (N) domain and the C-terminal F-actin-binding (C) domain. Top, α-catenin adopts an active, open conformation and binds to vinculin (purple) when the pulling force generated by trans-dimerization of E-cadherin and actomyosin-mediated high tension. Bottom, α-catenin adopts an autoinhibited conformation when it experiences little to no tension. The central modulatory domain, M fragment, is autoinhibited from interacting with various binding partners, such as the F-actin-binding protein vinculin. B, conformational change of vinculin-binding domain (MI, show in red and purple) in α-catenin between two structurally known states as follows: closed (autoinhibited) state (left, PDB code 4IGG) (35) and open (activated) state (right, PDB code 4EHP) (40) upon vinculin binding. Vinculin is shown in cyan in the complex (right).