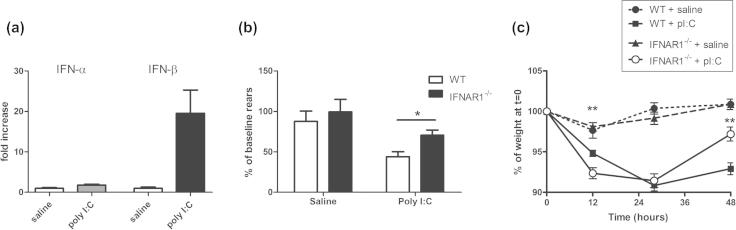
Fig. 2.
Poly I:C-induced type I interferons and sickness behaviour in WT and IFNAR1−/− mice. (a) The hypothalamic transcription of IFN-α and IFN-β were assessed at 6 h post-poly I:C (12 mg/kg i.p.). (b) The sickness behaviour response of C57BL/6 and IFNAR1−/− mice to poly I:C was assessed (b) open field rearing activity and (c) % body weight loss. Differential effects of poly I:C on (b) rearing were assessed using two-way ANOVA (with strain and treatment as between-subjects factors) and (c) body weight was assessed using 3 way ANOVA analysis with time, treatment and strain as factors in WT and IFNAR1−/− mice. Data are expressed as mean ± SEM, n = 5 for WT + saline, n = 8 for WT + pI:C, n = 13 for IFNAR1−/− + saline and n = 14 for IFNAR1−/− + pI:C. Full ANOVA analysis appears in the main text. Statistically significant differences by Bonferroni post-hoc are denoted by ∗∗p < 0.01 and ∗p < 0.05 w.r.t WT + pI:C .