Figure 8.
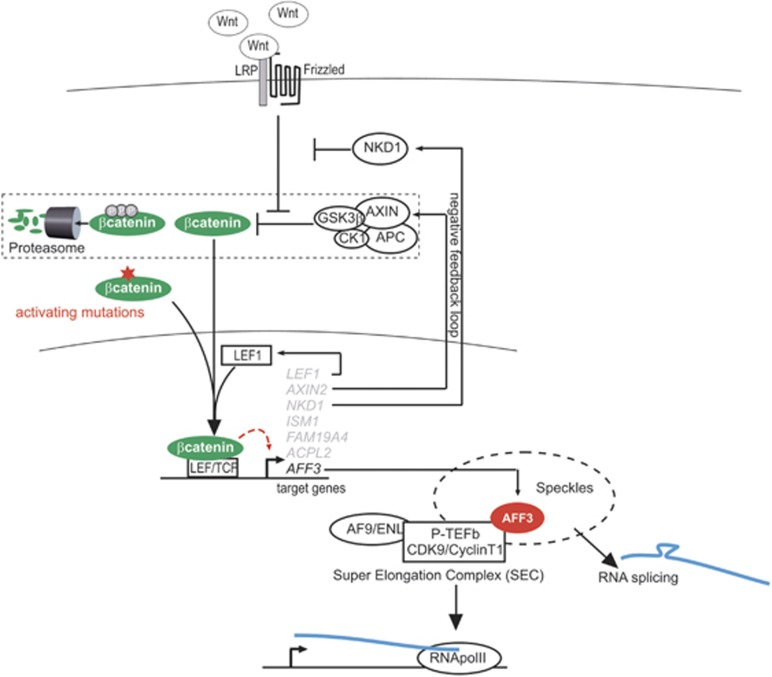
Target genes of the Wnt/β-catenin pathway in adrenocortical carcinoma. In the absence of Wnt factors, β-catenin is phosphorylated by GSK3β and CK1α as part of a multiprotein complex. Phosphorylated β-catenin is then degraded by proteasomes. In the presence of Wnt factors, Wnt binds to its frizzed receptor inhibiting the degradation complex that leads to cytoplasmic accumulation of β-catenin. Then, β-catenin migrates to the nucleus and associates with the LEF/TCF transcription factor to induce transcription of specific target genes. The CTNNB1 mutation leads to a constitutive transcriptional activity of β-catenin-LEF/TCF. Here, we have identified candidate genes regulated by the Wnt/β-catenin pathway in adrenocortical carcinoma. Among these genes, we identified AFF3 as a direct target of the Wnt/β-catenin pathway. AFF3 is localized in nuclear speckles and is associated with P-TEFb. AFF3 may have a role in adrenocortical tumorigenesis by acting on transcription and RNA splicing. Two genes may regulate the Wnt/β-catenin pathway: LEF1 may participate in transcriptional activation and NKD1 has been described as negative regulator. It might be also interesting to study the roles, if any, of FAM19A4, ACPL2 and ISM1 in adrenocortical tumorigenesis.