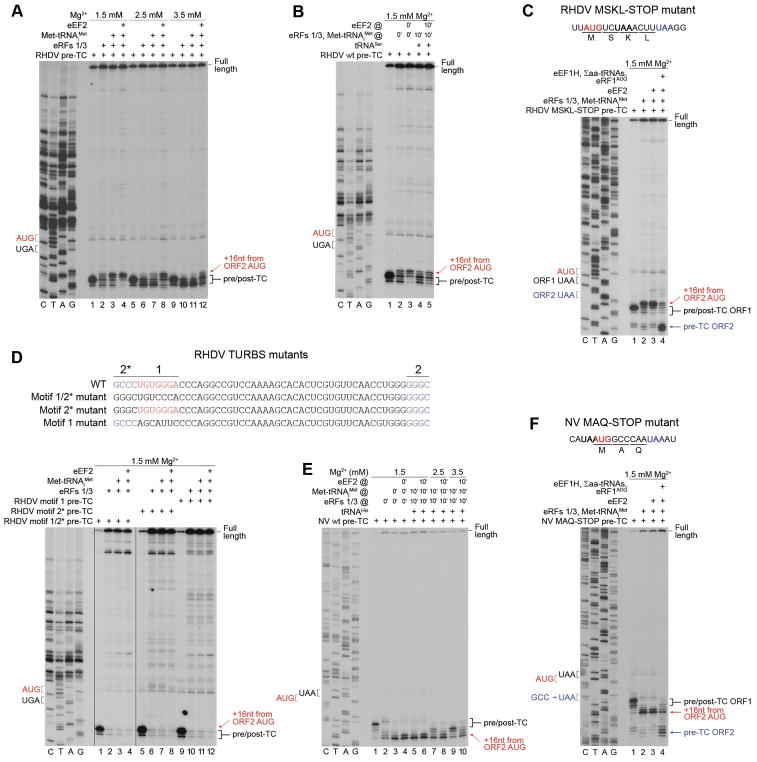
Figure 3. Reinitiation by post-termination ribosomes on model RHDV and NV mRNAs.
(A) Toe-printing analysis of reinitiation by post-termination ribosomes on RHDV mRNA, depending on [Mg2+] and the presence of eEF2. (B) The influence of preincubation of pre-TCs with deacylated tRNA on reinitiation by post-termination ribosomes on RHDV mRNA. (C) Toe-printing analysis of the ability of reinitiation complexes formed on RHDV mRNA to undergo elongation, assayed using “MSKL-STOP” mutant mRNA. (D) Toe-printing analysis of reinitiation by post-termination ribosomes on RHDV TURBS mutant mRNAs, containing substitutions in motifs 1 and 2*. (E) Toe-printing analysis of reinitiation by post-termination ribosomes on NV mRNA, depending on [Mg2+], the presence of eEF2, and preincubation of pre-TCs with deacylated tRNA. (F) Toe-printing analysis of the ability of reinitiation complexes formed on NV mRNA to undergo elongation, assayed using “MAQ-STOP” mutant mRNA. (A–F) Positions of pre/post-TCs on ORF1 (black brackets), 80S reinitiation complexes on ORF2 AUG (red arrows), and eRF1AGQ-associated pre-TCs on ORF2 (blue arrows) are shown on the right. Positions of stop (black or blue) and restart (red) codons are marked on the left. Free [Mg2+] is indicated on each panel. See also Figure S1.