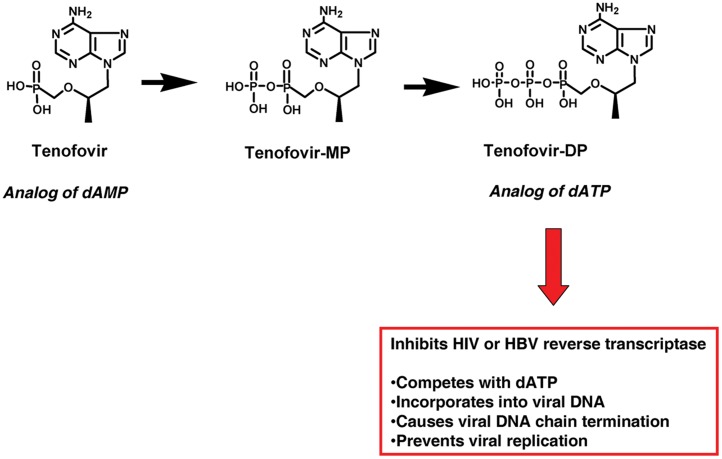
Figure 1. A scheme depicting intracellular activation, and the antiviral mechanism of action of tenofovir.
After transport into cells, tenofovir is phosphorylated in two steps by host nucleotide kinases to tenofovir-monophosphate (MP) and then tenofovir-DP, the active metabolite. Tenofovir inhibits viral replication by mechanisms indicated in the box.