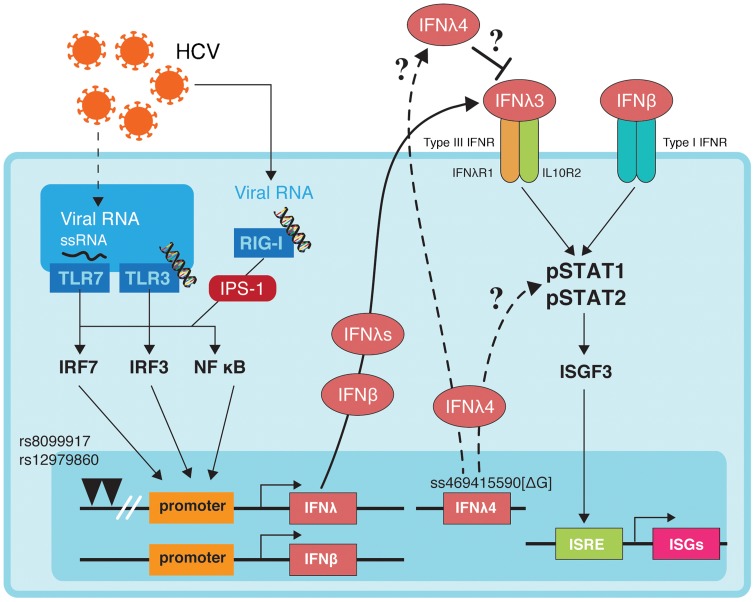
Figure 1. Host antiviral innate defense system proposed from in vitro experiments.
Upon viral infection, cytoplasmic viral sensors (RIG-I) and toll-like receptors (TLRs) detect viral pathogens, which results in IFNβ and IFNλs gene activation via the adaptor molecule IPS-1. IFNβ binds to type I IFN receptors, whereas IFNλs bind to type III IFN receptors comprising IL10R–IL28R receptor complexes. Both receptors activate the Jak–STAT pathway, which upregulates a large number of ISGs by activating the IFN-stimulated response element (ISRE). IL28B promoter activity is reportedly lower with unfavorable IL28B SNPs.RIG-I and ISG expressions in patients with unfavorable IL28B genotypes tend to be high at baseline and are insufficiently induced by exogenous IFN administration, resulting in poor treatment outcomes with IFN-based therapy. IFNλ4 is created by ss469415590 variant (ΔG), which is in high linkage disequilibrium with rs12979860. Although IFNλ4 induces ISGs by activating ISRE, this preactivation of IFN signaling impairs HCV clearance and prevents further activation by exogenous type I and type III IFNs.