Fig. 2.
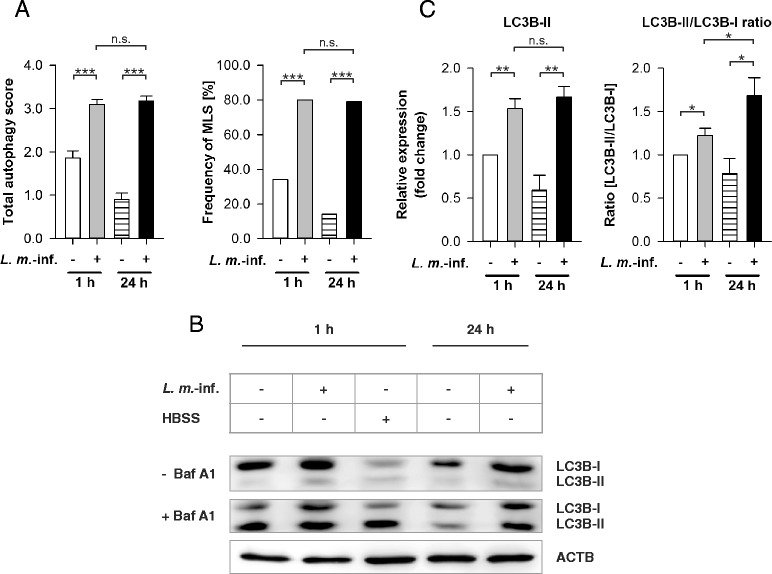
Autophagy assessment in L. m.-infected BMDM with TEM and LC3B western blot analyses. Methods: (a–c) BMDM from BALB/c mice were infected with L. m. promastigotes for 1 h or 24 h. Uninfected control BMDM were incubated for the same amount of time in RPMI medium. a All BMDM were subjected to TEM analyses. 50 BMDM from each sample were semiquantitatively analyzed for the grade of vacuolization (0 – 3) and the presence of MLS (+1), which resulted in a total autophagy score (maximum = 4). The total autophagy score and frequency of MLS were calculated. b, c Additionally, proteins were isolated from L. m.-infected and uninfected BMDM as well as from HBSS-starved BMDM to monitor autophagy with LC3B western blotting. Cell cultures were partially treated with Baf A1 to monitor autophagic flux. Western blots with proteins from 3 independent experiments were analyzed densitometrically. ACTB served as the internal loading control. Results: (a) The total autophagy score and the frequency of MLS were significantly increased in L. m.-infected BMDM 1 and 24 h p.i. compared to uninfected controls. There were no significant differences between L. m.-infected BMDM 1 and 24 h p.i.. b LC3B-II levels in samples from L. m.-infected BMDM 1 and 24 h p.i. were increased compared to uninfected controls. An accumulation of LC3B-II was visible in all Baf A1-treated samples (+ Baf A1) compared to controls (− Baf A1), which indicates an autophagic flux. c Results of densitometric analyses showed that LC3B-II levels and the LC3B-II/LC3B-I ratios were significantly increased in L. m.-infected BMDM 1 and 24 h p.i. compared to uninfected controls. Furthermore, the LC3B-II/LC3B-I ratio of L. m.-infected BMDM 24 h p.i. compared to 1 h p.i. was significantly increased. Baf A1 = Bafilomycin A1, L. m.-inf. = L. m.-infected, n.s. = not significant, * p ≤ 0.05, ** p ≤ 0.01, *** p ≤ 0.001
