Fig. 6.
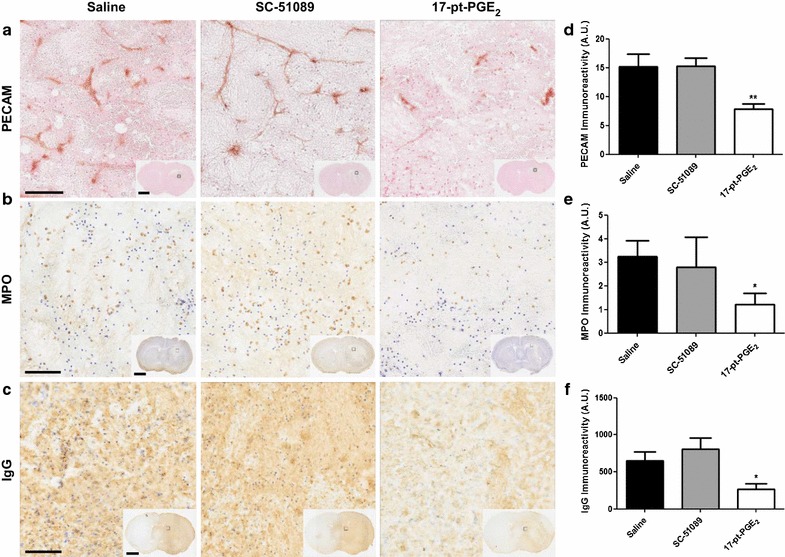
PECAM-1, MPO, and IgG immunoreactivity following ICH and blockade or stimulation of the EP1 receptor. Antagonist (SC-51089, 10 µg/kg), agonist (17-pt-PGE2, 0.3 mg/kg), or vehicle (saline) was administered subcutaneously at the onset of injury, 6 h post-ICH, and at 12-h intervals thereafter. Seventy-two hours after ICH, brains were harvested and sections processed for PECAM-1, MPO, and IgG immunohistochemistry to evaluate leukocyte transendothelial migratory potential, neutrophil infiltration, and BBB breakdown, respectively. a, b, c Representative high magnification photomicrographs showing a PECAM-1 staining highlighting blood vessels within the lesion, b MPO-positive neutrophils within the lesion, and c IgG staining within the lesion and surrounding areas of coronal brain sections from control (left panels), SC-51089- (middle panels), and 17-pt-PGE2- (right panels) treated mice. Square selections in the insets denote magnified regions. Scale bars on the magnified images and inserts are 100 µm and 2 mm, respectively. d, e, f Quantification revealed that 17-pt-PGE2-treated mice had significantly less d PECAM-1 staining, e neutrophil infiltration, and f BBB breakdown. All quantification data are presented at the same scale such that the relative d PECAM-1, e MPO, and f IgG immunoreactivity can be directly compared. No significant differences were seen for the SC-51089-treated mice. *p < 0.05 and **p < 0.01 when compared to the control group, n = 7–10 per group.
