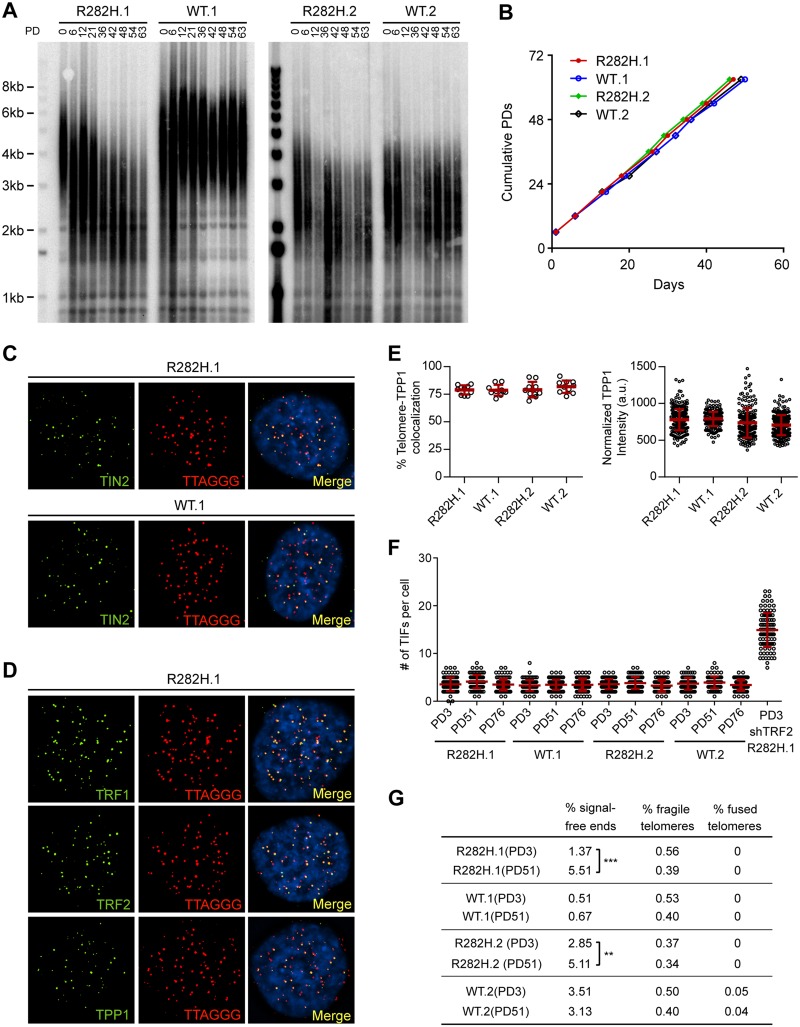
Fig 1. Heterozygous TIN2-R282H mutation induces progressive telomere shortening, but not gross telomere deprotection, in HCT116 cells.
(A) Telomeres were maintained in cells with wild-type TIN2, but progressively shortened in cells with heterozygous TIN2-R282H mutation. Cells were continuously passaged and collected at the indicated population doublings (PD). Genomic DNAs were extracted and bulk telomere lengths were examined by Telomere Restriction Fragment analysis using a telomeric repeat probe. (B) Growth curve of HCT116 knock-in cells. (C) Telomeric localization of TIN2 examined by immunofluorescence-FISH analysis in cells carrying heterozygous TIN2 mutation (clone R282H.1, PD8 cells) and wild-type TIN2 (clone WT.1, PD8 cells). For immunofluorescence staining, we used an anti-TIN2 antibody (Imgenex) (produced against an N-terminal epitope of TIN2 (a.a. 44–58)) which recognizes both the wild-type and mutant TIN2. Telomeres were detected by FISH using a PNA telomeric probe. (D) Telomeric localization of TRF1, TRF2 and TPP1 examined by immunofluorescence-FISH analysis in cells carrying heterozygous TIN2 mutation (clone R282H.1, PD8 cells). (E) Left panel: quantification of fraction of telomeres co-localizing with TPP1. Each circle on the graph represents a single nucleus. Telomeres in 10 nuclei were examined for each knock-in clone. Mean ± SD indicated by red lines. Right panel: TPP1 fluorescence intensity, normalized against telomere length (based on telomere FISH signal intensity). Each circle on the graph represents a single telomere. Mean ± SD indicated by red lines. Telomeres in 10 nuclei were analyzed for each clone. (F) Quantification of telomere dysfunction-induced DNA damage foci (TIFs) in early (PD3) and late PD (PD51 and PD76) HCT116 knock-in clones. For positive control, R282H.1 cells were treated with shRNA against TRF2 and TIFs quantified. DNA damage was assessed by immunostaining with an antibody against 53BP1 and telomeres were detected by PNA FISH using a telomeric probe. All quantifications were carried out blindly. Each circle on the graph represents a single cell. Mean ± SD indicated by red lines. TIFs in 100 cells were analyzed for each sample. (G) Quantification of telomeric abnormalities from metaphase spreads of HCT116 knock-in clones. Cells were collected at indicated PDs for metaphase spreading followed by FISH analysis using a PNA telomeric probe and a centromeric probe. ~4000 telomeres were analyzed for each sample. All quantifications were carried out blindly.