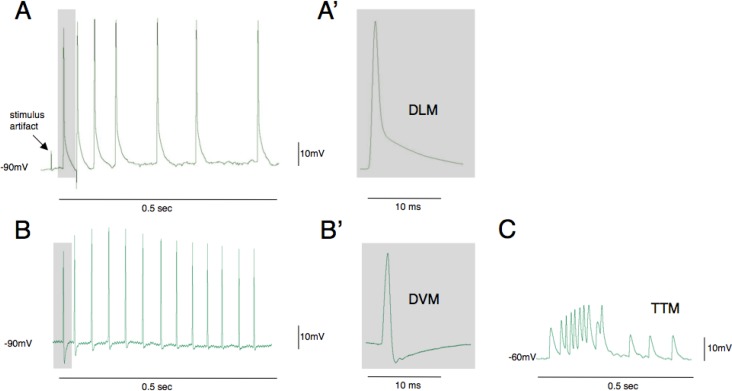
Figure 3.
Action potential waveforms evoked by optogenetic activation of the escape circuit. The most conspicuous muscle fibers in the thorax are dorsal longitudinal muscles (DLMs) and these are most frequently impaled when electrodes are inserted using this preparation (A, A′). The cells have highly negative resting potentials (−90mV) and are easiest to maintain recording as contractions are evoked. Dorsal ventral muscles (DVMs) are also frequently recorded from and are identified by their large after hyperpolarization potential (B, B′). The tergotrochanteral (TTM) jump muscles have much more positive resting potentials and lower amplitude action potentials (C). Traces in B and C are from student data.