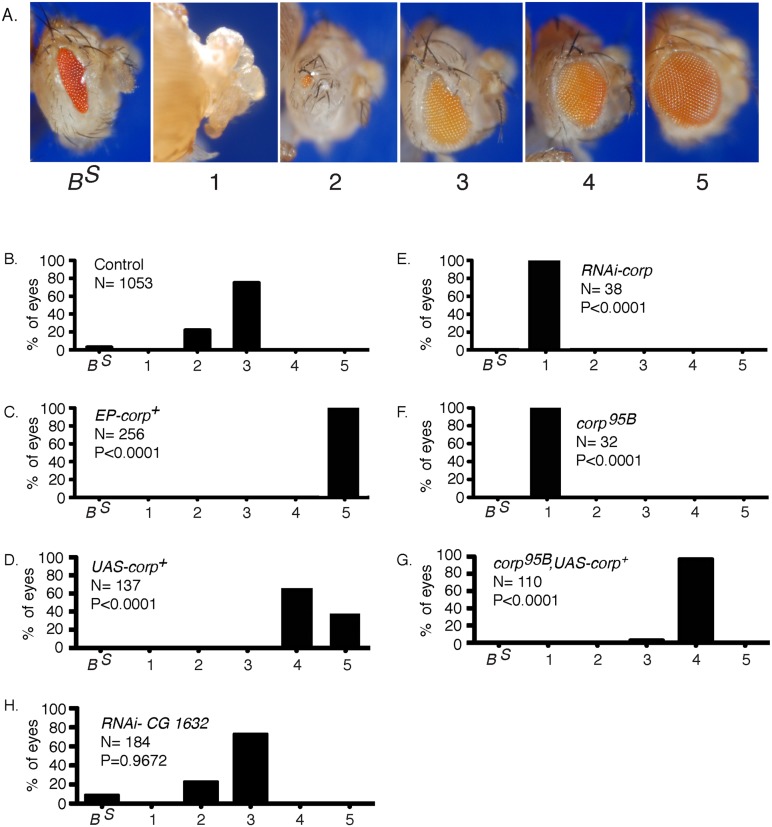
Fig 2. Overexpression of corp + suppresses the BARTL phenotype.
(A) The range of eye phenotypes observed in the assay. The B S phenotype of H1 control males is shown at the left. When FLP is expressed (ey>FLP), the phenotypes can range from headless pharates (category 1) to adults with a fully developed wildtype eye (category 5). The distribution produced (B) in control males; (C) in males carrying P{EPgy2}EY03495, referred to as EP-corp +; (D) by inclusion of a UAS-corp + transgene; (E) with RNAi-mediated knockdown of corp; (F) in corp 95B mutants; (G) with rescue of the corp 95B phenotype by expression from the UAS-corp + transgene; and, (H) with RNAi-mediated knockdown of CG1632. N represents number of eyes scored for each genotype. Each P value represents comparison with the wildtype control, shown in B. Genotypes were: (B) y w/H1; eyGal4 UAS-FLP/+; (C) y w EP-corp + /H1; eyGal4 UAS-FLP/+; (D) y w/H1; eyGal4 UAS-FLP/+; UAS-corp + /+; (E) y w/H1; eyGal4 UAS-FLP/RNAi-corp; (F) y w corp 95B /H1; eyGal4 UAS-FLP/+; (G) y w corp 95B /H1; eyGal4 UAS-FLP/+; UAS-corp + /+; (H) y w/H1; eyGal4 UAS-FLP/RNAi-CG1632.