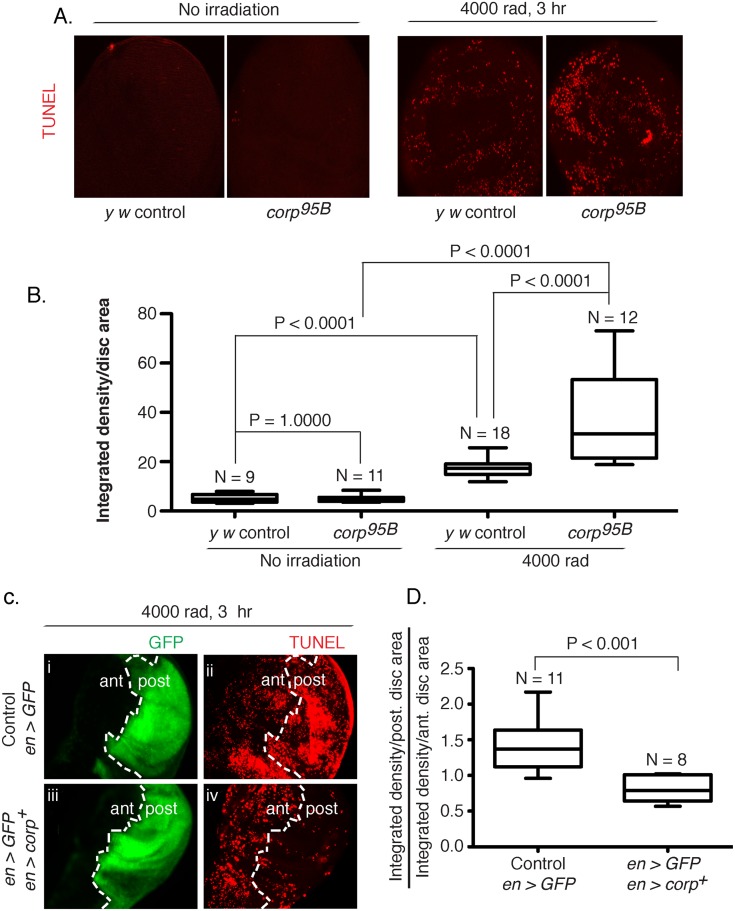
Fig 3. Corp inhibits DNA damage-induced apoptosis in somatic tissue.
(A-B) The effect of the corp 95B mutant assayed by TUNEL staining of wing discs from third instar larvae with or without exposure to irradiation (IR). Very little apoptosis was detected in control or mutant genotypes without irradiation, but staining is greatly increased 3 hours after 4000 rads of irradiation, and corp 95B mutants exhibit significantly more staining than the y w control. Images were captured with a 20X objective at 800 ms shutter speed. (B) Quantitation. Intensity of TUNEL staining is measured as Integrated density (InD = total pixel intensity in the selected region) per unit area of wing disc for y w control and corp 95B mutant, with and without irradiation. N represents total number of discs used for quantification. (C-D) The effect of corp + overexpression on cell death is assayed by TUNEL staining of third instar wing discs 3 hours after exposure to 4000 rads of IR. The white broken line marks the boundary between the anterior (ant) and posterior (post) compartments of the disc, based on engrailed-driven GFP fluorescence that marks the posterior compartment (i and iii). (i, ii) The staining pattern in wildtype control. (iii, iv) Staining in discs where engrailed is driving EP-corp + overexpression in posterior compartment. TUNEL staining is dense in wildtype larvae in the posterior segment (ii), but is greatly reduced with corp + overexpression (iv). All images were taken with a 20X objective at 500 ms shutter speed. (D) Quantitation. InD per unit area was measured individually for the anterior and posterior compartment of each disc and the Y-axis is denoted as a ratio of InD per unit area of the posterior compartment to that of the anterior compartment. Genotypes tested are indicated on the X-axis. N represents total number of discs used for quantification.