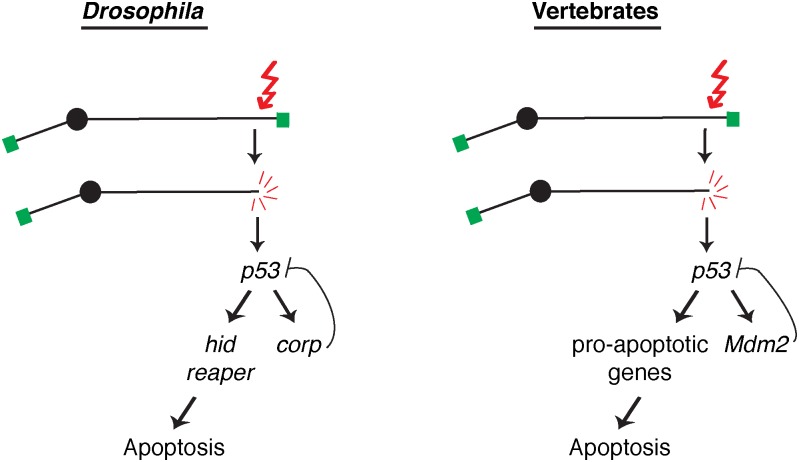
Fig 7. A comparison of competing pathways under P53 control in Drosophila and vertebrates.
A DNA double-strand break activates the DNA damage response leading to activation of P53. In Drosophila, transcription of the well-known pro-apoptotic genes hid and reaper is activated in one pathway downstream from P53, while transcription of the anti-apoptotic gene corp is activated in a second downstream pathway that constitutes a negative feedback loop on P53. These competing pathways are analogous to those found in vertebrates, where P53 promotes apoptosis by inducing a variety of pro-apoptotic genes in one pathway and the P53 negative regulator Mdm2 in a competing branch. Altering the activity of these competing pathways alters the life or death outcome initiated by the DNA damage signal.