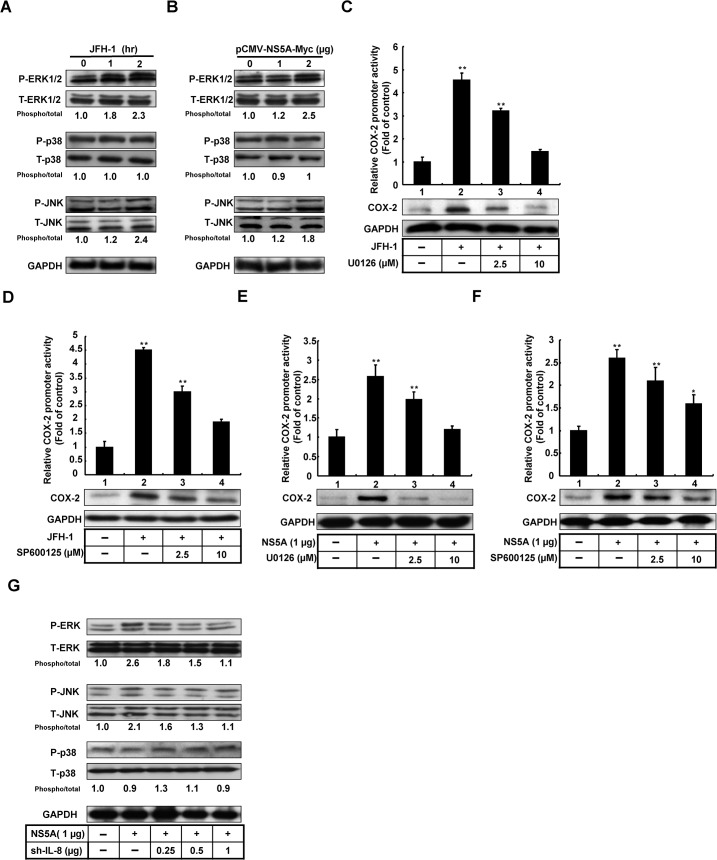
Fig 4. Analysis of the effects of ERK and JNK signaling pathways on COX-2 expression mediated by HCV.
(A, B) Huh7 cells were infected with HCV JFH-1 or transfected with pCMV-NS5A-Myc. Following infection or transfection, the cells were grown in complete medium. The cell lysates were collected and subjected to western blotting with specific antibodies for MAPK (ERK, p38, and JNK) and phospho-MAPK. (C-F) To identify the COX-2 activation through ERK and JNK activation upon HCV NS5A expression or HCV infection, Huh7 cells were co-transfected with pCOX-2-Luc with pCMV-NS5A-Myc or infected with HCV JFH-1. Following transfection or infection, the cells were grown in complete medium with or without the specific ERK inhibitor U0126 and JNK inhibitor SP600125. The cell lysates were collected and subjected to the luciferase activity assay to measure COX-2 promoter activity and western blotting with antibodies specific for COX-2 and GAPDH. (G) Huh7 cells were co-transfected with pCMV-NS5A-Myc (1 μg), and different amounts of IL-8 shRNA (0–1 μg). After 3 days, the cell lysates were collected and subjected to western blotting with antibodies specific for MAPK (ERK, p38, and JNK) and phospho-MAPK. GAPDH was used an equal loading. Data shown are mean ± SE; n = 3. *p < 0.05. **p < 0.01.