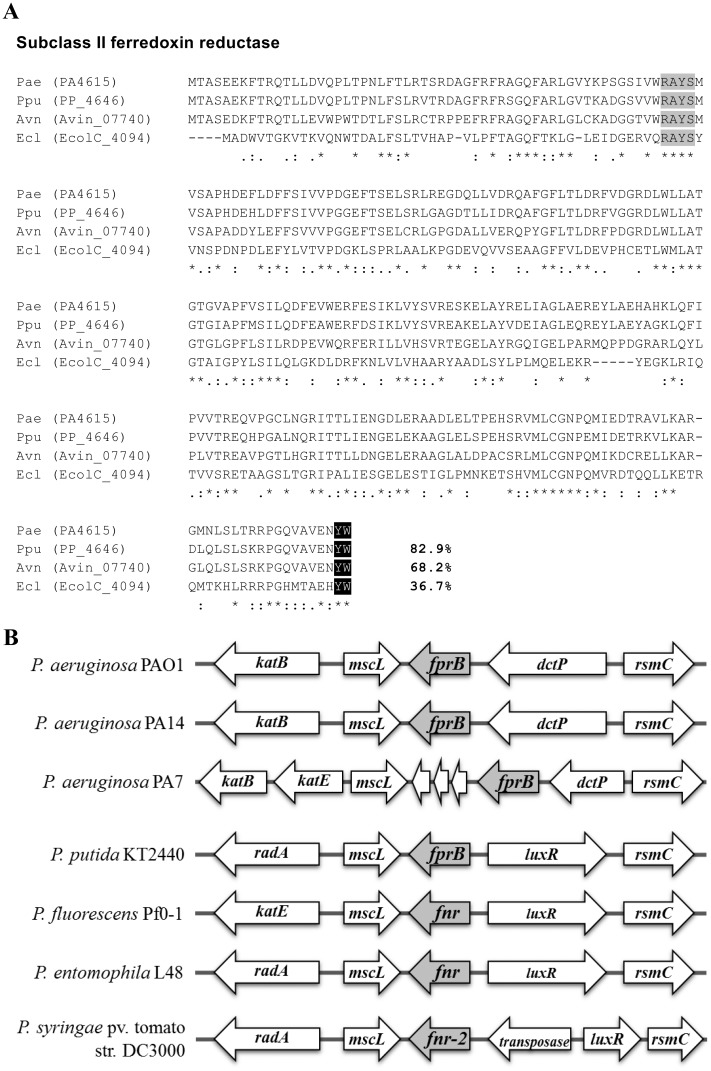
Fig 1. Multiple amino acid sequence alignment and gene organization of P. aeruginosa fprB.
(A) Alignment of P. aeruginosa FprB with other characterized bacterial FprB enzymes (Ppu, P. putida; Avn, A. vinelandii; and Ecl, E. coli ATCC 8739) was performed using the CLUSTALW program [57]. Black (YW) and light gray (RAYS) boxes indicate the subclass II signature amino acid and the FAD-binding domain, respectively. The asterisk, colon, and period symbols indicate identical residues, conserved substitutions, and semi-conserved substitutions, respectively. Number indicates percent identity of the aligned protein with that of P. aeruginosa. (B) Gene organization at the fprB locus among Pseudomonas spp. fnr and fnr-2, fprB-homologous genes; katB and katE, catalase genes; mscL, gene encoding large conductance mechanosensitive channel; dctP, gene encoding propable periplasmic C4-dicarboxylate binding-protein; rsmC, gene encoding propable 16S RNA G1207 methylase; luxR, LuxR family DNA-binding transcriptional regulator gene; radA, gene encoding propable DNA repair protein; non-labelled, gene with unknown annotation.