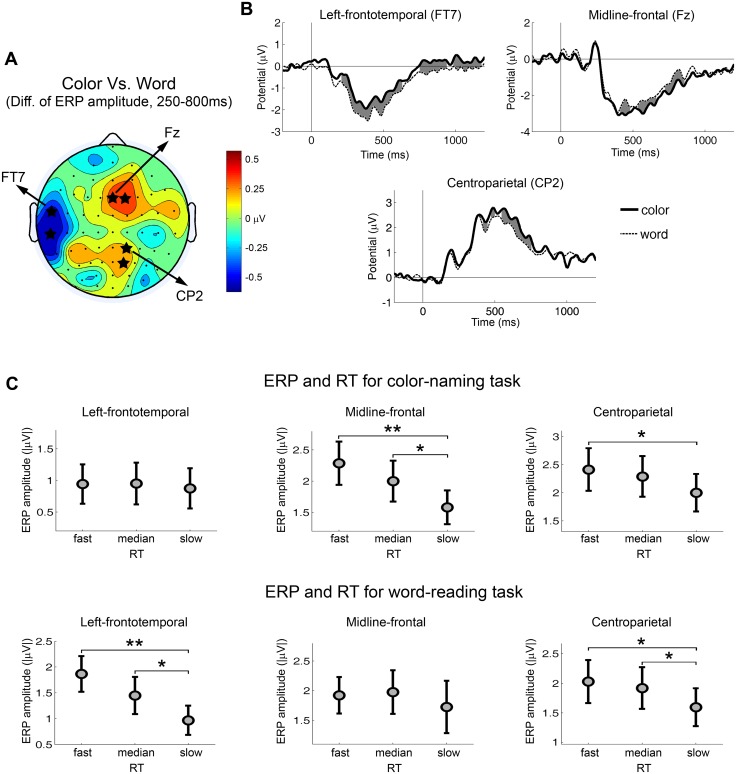
Fig 2. Task-related ERPs and their associations with reaction time.
(A) Topography of the ERP difference from the contrast of color-naming versus word-reading trials. Blue color indicates larger ERPs for word-reading trials. Red color indicates larger ERPs for color-naming trials. The value that was used to compute the difference was the mean ERP amplitude within the period of 250–800 ms after the cue onset. The electrodes with significant ERP difference across subjects were marked by stars (p < 0.05). (B) Cue-evoked ERP waveforms from electrodes in the left-frontotemporal, the midline-frontal and the centroparietal scalp regions for color-naming trials and word-reading trials. Time zero is the cue onset. The time periods with significant ERP difference across subjects were shaded by gray color (p < 0.05). (C) ERP amplitudes for different RT groups by task type. Significant differences between RT groups were marked (** p < 0.01, * p < 0.05).