Figure 4.
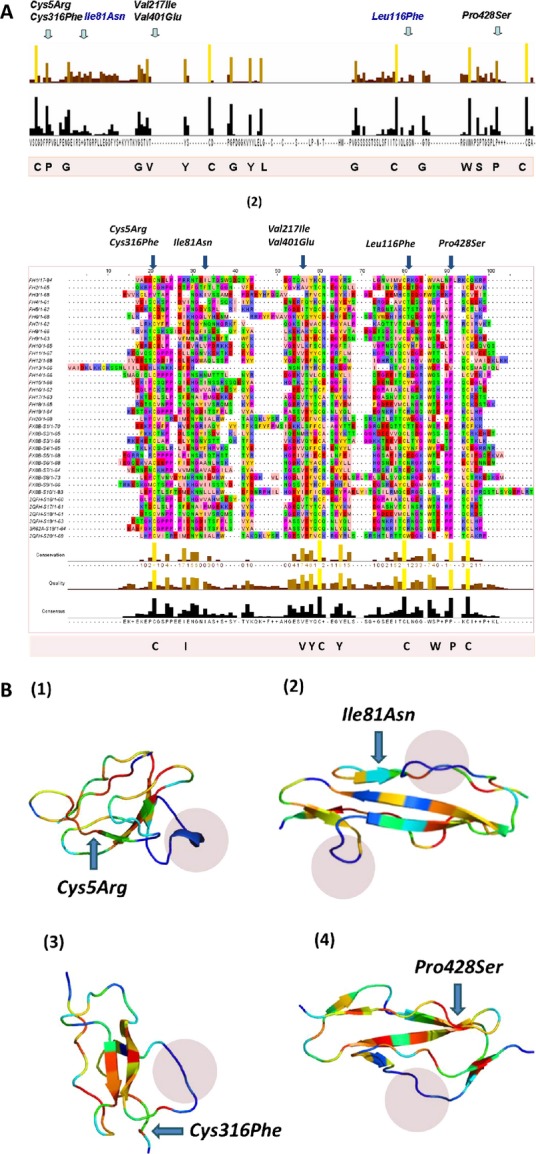
Sequence and structural conservation of sushi domains. A(1) Conservation results for the multiple sequence alignment of FXIIIB subunit sushi domains with sushi domains from 50 mammalian sushi domain-containing proteins. Owing to the large size of the actual alignment, it is not shown here. Only the conservation has been shown here with two bar graphs. The upper colored one depicts the degree of conservation and the lower bars show the consensus. Taller bars indicate higher sequence identity and also conservation. A(2) Multiple sequence alignment of FXIIIB subunit sushi domains with sushi domains of the complement factor H. The highly conserved residues are colored and also listed at the bottom of the multiple sequence alignment. The residues corresponding to each mutation have been marked at the position they occur in the alignment. (B) Structural alignment results for four sushi domains on which the mutations Cys5Arg (S1; B1), Ile81Asn (S2; B2), Cys316Phe (S6; B3) and Pro428Ser (S7; B4) occur. Structural conservation is depicted in a color gradient where blue represents lowest conservation level and red the highest. The variable length loops connecting the beta strands, which show the highest structural variability, are shown in blue shaded regions in each domain.
