Figure 6.
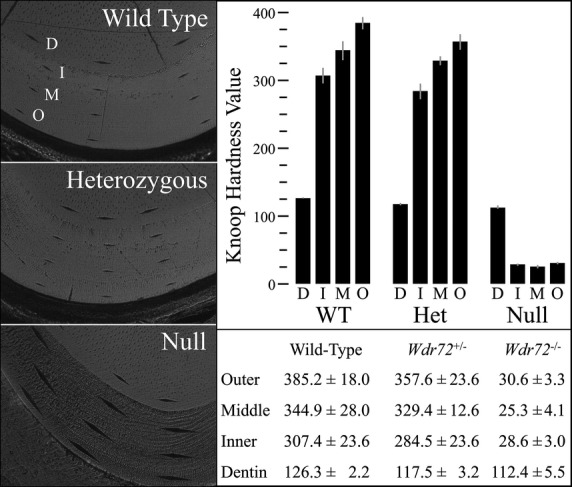
Knoop hardness testing of 7-week mandibular incisors. The left panel shows indentations made by a 10-gm force application in incisor cross-sections at the level of alveolar crest (level 8) for the three genotypes. The hardnesses of the dentin (D), and the outer (O), middle (M), and inner (I) enamel were evaluated. Three indentations were generated at each sample level and measured to calculate the Knoop hardness values (HKs). The right lower panel demonstrates the mean HKs over different areas of different genotypes, and the comparative histograms are presented at the right upper panel. In the wild-type and heterozygous mutant, the HKs of enamel gradually increased from inner to outer areas and are averaged 2.7-fold greater than the measured HK of dentin. In contrast, The Wdr72−/− enamel exhibited significantly reduced HK values, which averaged only 25% of those for dentin and 10% of those for wild-type enamel.
