Table 1.
A summary of the scientific evidence for variables with sufficient data to draw a conclusion on the association between work environment factors and future depressive symptoms
| Work-related factor | Participants | Studies | Scientific evidence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Relationship between occupational environment and less depressive symptoms | |||
| Control | 158 251 | 19 |
|
| Relationship between occupational environment and more depressive symptoms | |||
| Demands - psychological job demands | 53 985 | 10 |
|
| Job strain | 197 682 | 14 |
|
| Passive job (low decision latitude, low job demands) | 11 419 | 2 |
|
| High pressure job | 34 554 | 5 |
|
| Effort reward imbalance | 27 136 | 3 |
|
| Low support at the work place | 82 772 | 17 |
|
| - Low supervisor support | 50 935 | 8 |
|
| - Low co-worker support | 27 170 | 6 |
|
| Poor social climate at the work place | 9 242 | 2 |
|
| Poor social capital at the work place | 59 340 | 2 |
|
| Low work place justice | 33 589 | 5 |
|
| - Procedural injustice | 33 589 | 5 |
|
| - Relational injustice | 30 761 | 3 |
|
| Work place conflicts | 13 732 | 3 |
|
| - Conflicts with superiors | 9 692 | 2 |
|
| - Conflicts with co-workers | 9 692 | 2 |
|
| Bullying | 15 173 | 3 |
|
| Low job development | 15 173 | 4 |
|
| Job insecurity | 24 833 | 7 |
|
| Long working week | 13 107 | 6 |
|
The scientific evidence is in-sufficient (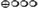 ) to determine if there is a relationship between the following occupational factors and depressive symptoms/ ) to determine if there is a relationship between the following occupational factors and depressive symptoms/ | |||
| Demands (several types of demands), Demands (emotional), Distributive justice, Threats, Violence, Irregular, Irregular work hours, Physically demanding work, Pesticides, Solvents, Heavy metals | |||
 - There is scientific evidence for an association between exposure and outcome. The result is based on studies of high or moderate quality. The quality of evidence has been upgraded due to consistency of the data (control and job strain) or large magnitude of effect (bullying)
- There is scientific evidence for an association between exposure and outcome. The result is based on studies of high or moderate quality. The quality of evidence has been upgraded due to consistency of the data (control and job strain) or large magnitude of effect (bullying)
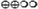 - There is scientific evidence for an association between exposure and outcome. The result is based on studies of high or moderate quality
- There is scientific evidence for an association between exposure and outcome. The result is based on studies of high or moderate quality
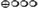 - It is not possible to determine if there is any association between exposure and outcome. The motivation is that one or several conditions apply: 1) no study fulfilled the inclusion criteria, 2) none of the studies fulfilling the inclusion criteria were relevant to the hypothesis tested in the present review, 3) all relevant studies were of low quality or 4) studies were of high or moderate quality - but one or several limitations applied, e.g. inconsistency of data between studies
- It is not possible to determine if there is any association between exposure and outcome. The motivation is that one or several conditions apply: 1) no study fulfilled the inclusion criteria, 2) none of the studies fulfilling the inclusion criteria were relevant to the hypothesis tested in the present review, 3) all relevant studies were of low quality or 4) studies were of high or moderate quality - but one or several limitations applied, e.g. inconsistency of data between studies
