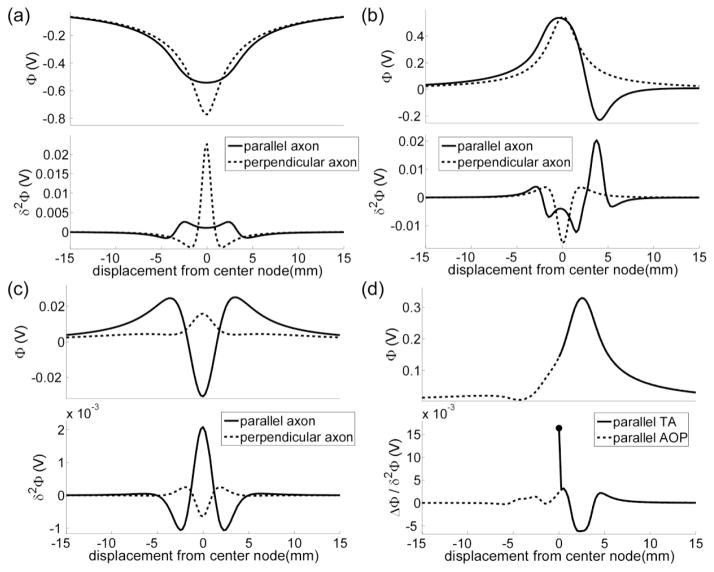
Figure 10.
The effect of electrode geometry and polarity on the force driving polarization of the neural membrane. Shown are the potentials and second difference of the potentials (δ2Φ) generated by (a) a long cylindrical electrode (figure 4a), (b) an asymmetric bipole (figure 5a), (c) a guarded cathode (figure 8a), and (d) a distal anode (figure 6a) across the nodes of Ranvier of an axon of passage (AOP). The filled circle in d denotes the first difference of the potentials (ΔΦ) at the terminal of a terminating axon (TA).