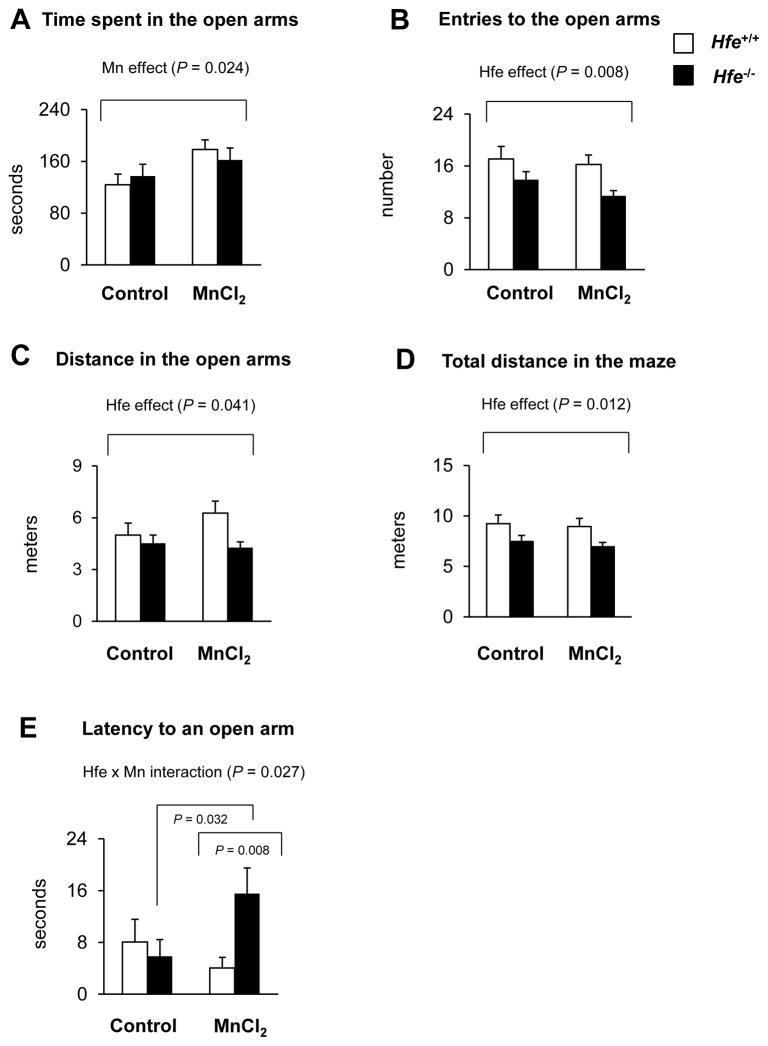
Figure 4. Effect of intranasal manganese on emotional behavior in Hfe-deficient mice.
Mice intranasally instilled with MnCl2 (5 mg/kg, daily) or water for 3 weeks were tested on the elevated plus maze in order to determine anxiety- and impulsivity-related behavior, including time in the open arms (A), entries to the open arms (B), distance in the open arms (C), total distance in the whole maze (D) and latency of the first entry to an open arm (E). Empty and closed bars represent wild-type (Hfe+/+) and Hfe-deficient (Hfe−/−) mice, respectively. Data were presented as mean ± SEM (n = 10–13 per group) and were analyzed using two-way ANOVA, followed by post-hoc comparisons.