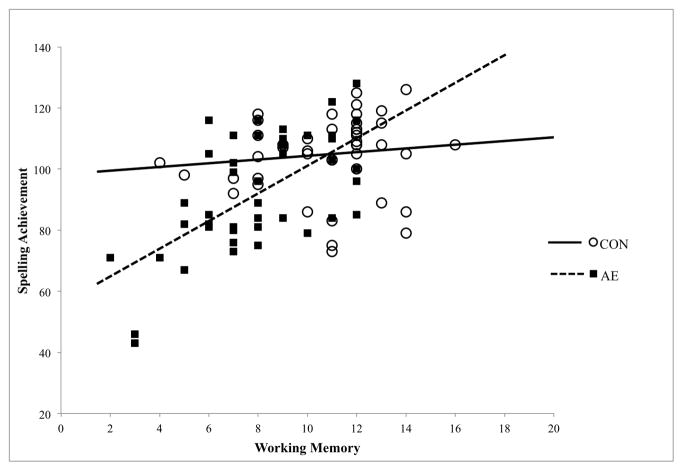
Figure 1.
Relation between working memory (NEPSY-II scaled score) and spelling achievement (WIAT-II standard score) for children with heavy prenatal alcohol exposure (AE), and non-exposed control children (CON). A significant working memory x group interaction and follow up analyses indicated that working memory significantly contributed to spelling achievement in the AE group (R2 = 0.386), but not in the control group (R2 = 0.014). The analyses have been rerun without the two lower AE subjects shown on the graph, and the results remain the same. See text for details.