FIGURE 6.
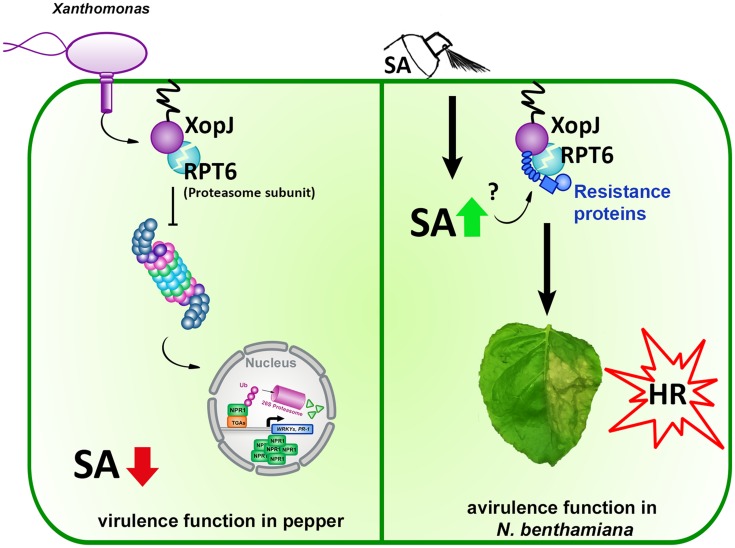
Model of XopJ’s virulence and avirulence (Avr) function in a host and non-host plant, respectively. (Left) pathogenic Xcv injects XopJ via its type-III secretion system into pepper host cells where it cleaves RPT6 to inhibit the proteasome. Reduced proteasomal activity interferes with the turnover of defense components, suppresses SA accumulation and results in the attenuation of SA-mediated defense responses. (Right) In the non-host plant N. benthamiana transiently expressed XopJ cleaves endogenous RPT6. When SA levels are increased by exogenous application of the defense hormone, R-protein mediated recognition of RPT6 cleavage by XopJ is activated leading to the induction of HR-like symptoms.