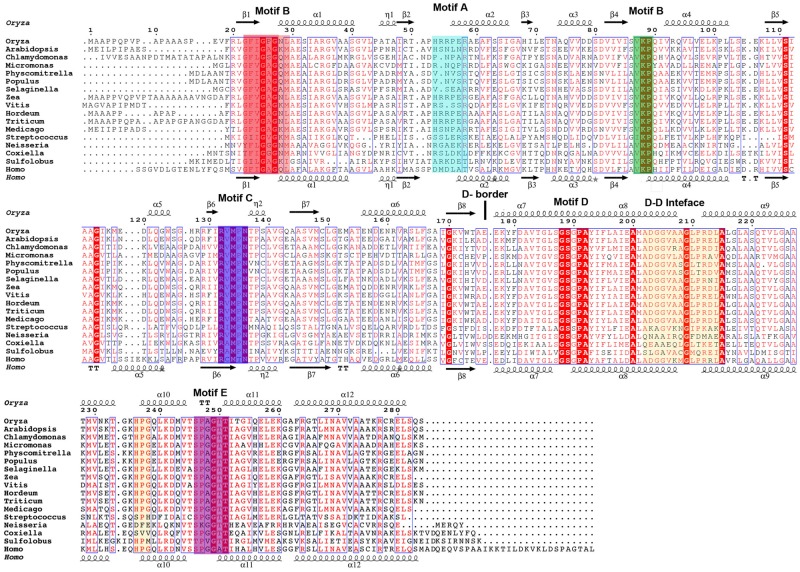
FIGURE 2.
Multiple sequence alignment of selected representatives of the P5CR family. For simplicity, 17 sequences of characterized and uncharacterized representatives of P5CRs have been aligned using Clustal W2 (Larkin et al., 2007) and Espript 3.0 (Robert and Gouet, 2014). Sequence identities are highlighted in red and similarities are displayed as red letters. The corresponding secondary structures of plant OsP5CR and human HsP5CR are shown on the top and the bottom (in black), respectively. Helices (α-helix; η-310 helix) appear as scribble, beta strands (β-strand) as arrows. Conserved fingerprint motifs are highlighted in color and labeled (Motif A, cyan; Motif B, red and green; Motif C, blue; Motif E, magenta; D–D, dimer–dimer interfaces in orange; D-border, border of domains). The following sequences were used, with the accession numbers and PDBid indicated in parentheses: Homo sapiens (P32322; 2GER); Sulfolobus solfataricus (Q97ZT3); Neisseria meningitides (Q9K1N1; 1YQG); Streptococcus pyogenes M1 GAS (Q9A1S9; 2AHR); Medicago truncatula (gi| 357509475); Triticum aestivum (gi| 58843559); Hordeum vulgare (gi| 326512934); Vitis vinifera (gi| 359482209); Zea mays (gi| 162459912); Selaginella moellendorffii (gi| 302811968); Populus trichocarpa (gi| 224086867); Physcomitrella patens (XP_001772037.1); Micromonas sp. RCC299 (gi| 255077536); Chlamydomonas reinhardtii (gi| 159478755, the first 60 residues were not aligned); Arabidopsis thaliana (NP_196984.1); Oryza sativa ssp. japonica (gi| 215695199).