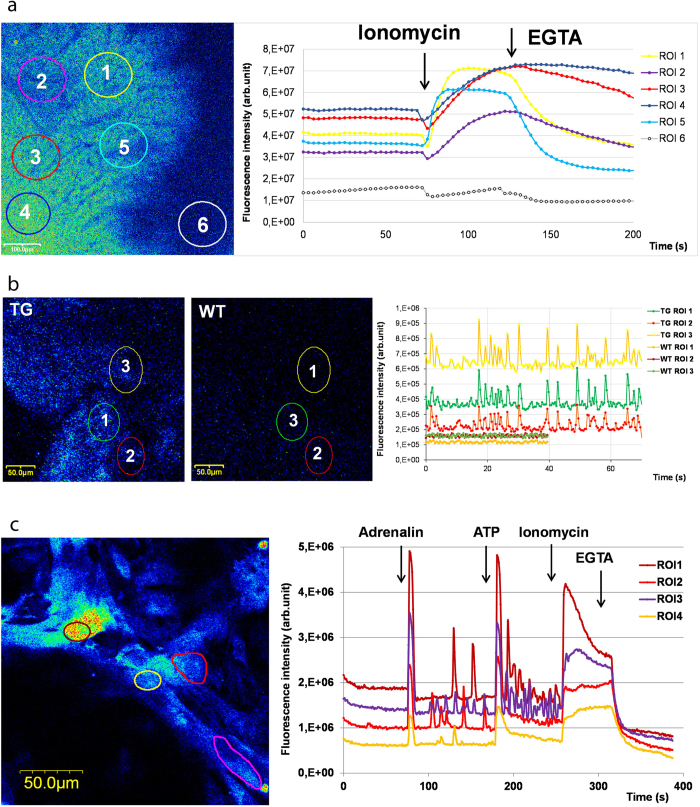
Figure 3. CAG-GCaMP2 expressing ventricular slices and cardiac cultures allow detection of spontaneous and ligand-induced calcium signals.
(A) The left panel shows the fluorescence image of a ventricular slice obtained from a transgenic rat heart with circled region of interest (ROI). The right panel shows the effect of ionomycin and EGTA administration on the kinetics of calcium signals in the indicated ROIs. (B) The left panel shows the fluorescence images of transgenic (TG) and wild type (WT) ventricular slices with circled region of interest (ROI). The right panel shows the fluorescence signals caused by spontaneous calcium waves in TG and WT ventricular slices in the indicated ROIs. (C) Spontaneous calcium oscillations were induced by adrenalin and ATP in ventricular cell cultures generated from GCaMP2 expressing rats. Cell cultures obtained from the heart of TG rats were treated with adrenalin, ATP, ionomycin and EGTA. Physiologically relevant ligands such as adrenalin or ATP evoked a strong increase in intracellular Ca2+ levels and both compounds induced spontaneous calcium oscillations after addition.