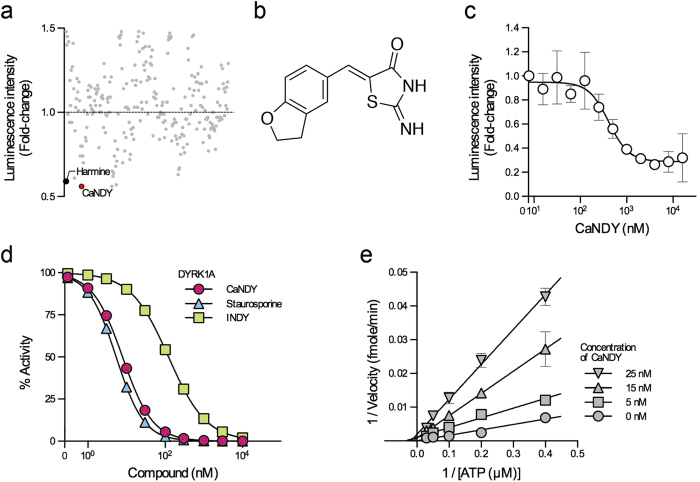
Figure 5. Identification of a potent inhibitor of DYRK1A.
(a) A total of 253 compounds from our original synthetic chemical library were examined. These compounds were used at 4 μM. Relative luminescence intensities are shown. Harmine was used as a positive control and is indicated by the black point. The red point indicates CaNDY. (b) Structure of CaNDY. (c) CaNDY antagonized the interaction between DYRK1A and CDC37 complex. 293T cells expressing CDC37-nanoKAZ were transiently transfected with an expression vector for 3xFLAG-DYRK1A (Y319F/Y321F) and then treated with the indicated concentrations of CaNDY. The points represent means ± SD (n = 3). Representative dose-response curves with Hill slopes are shown. (d) CaNDY inhibited the catalytic activity of DYRK1A in an in vitro kinase assay. Recombinant DYRK1A was incubated with the substrate peptide DYRKtide-F in the presence of the indicated concentrations of small molecules. CaNDY, INDY, and staurosporine inhibited the kinase activity with IC50 values of 7.9 nM, 122 nM, and 5.4 nM, respectively. Representative dose-response curves with Hill slopes are shown. (e) Double-reciprocal plots showing the competitive inhibition of ATP by CaNDY. DYRK1A kinase activity was measured at the indicated concentrations of CaNDY and ATP. Reciprocal velocity was plotted versus 1/[ATP]. Km = 14.1 μM and Ki = 1.92 nM.