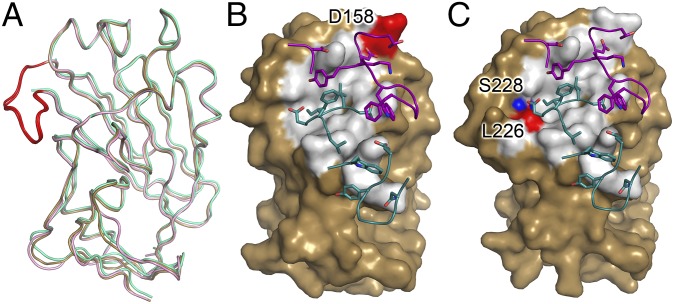
Fig. 3.
Comparison of H5.3 interfaces in H5hd-rdt complexes. (A) Overlay of wt_H5hd (gold), H5hd_rdt_Vn (green), and H5hd_rdt_In (light pink). The 220 loop is highlighted in red in the wt_H5hd and H5hd_rdt_In structures; the 220 loop is not visible in the H5hd_rdt_Vn structure. The surface rendering of H5 is rotated 20° relative to A and highlights the solvent inaccessible interface of H5.3 on H5hd_rdt_Vn (B) and H5hd_rdt_In (C). The rdt residues in the H5.3 interface are highlighted in red. The rdt residue not in the interface is highlighted in blue (T160A in H5hd_rdt_In is not visible in this view of the structure). The CDR loops of H5.3 are shown as loops, with the residues involved in the interface highlighted as sticks, with the heavy chain in teal and the light chain in purple.