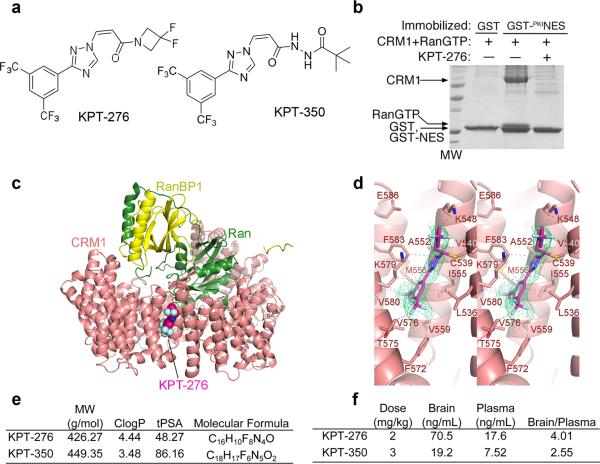
Figure 2. KPT selectively and covalently bind CRM1 and inhibit binding to NES with pharmacokinetic properties that favor blood brain barrier permeability.
(a) Chemical structure of KPT-276 and KPT-350. (b) Inhibition of CRM1-NES binding by KPT-276 due to direct blockade of the NES binding groove. Pull-down assay of ~15 μg of 10 μM HsCRM1 binding to either immobilized GST or GST-PKINES in the presence of RanGTP and either buffer or 100 μM KPT-276. (c) The 1.8 Å resolution crystal structure of KPT-276 bound to CRM1 showing KPT-276 binding in the NES-binding groove. (d) Magnified view of KPT-276 bound to CRM1 showing interactions between the inhibitor and CRM1 with the composite omit map of the inhibitor shown as a green mesh. (e) Pharmacological properties of KPT-276 and KPT-350 including molecular weight (MW), clogP (calculated logarithm of partition coefficient), topological polar surface area (tPSA) and molecular formula. (f) Pharmacokinetic properties of orally gavaged KPT-276 (2 mg/kg) and KPT-350 (3 mg/kg) in Sprague-Dawley rats.