Abstract
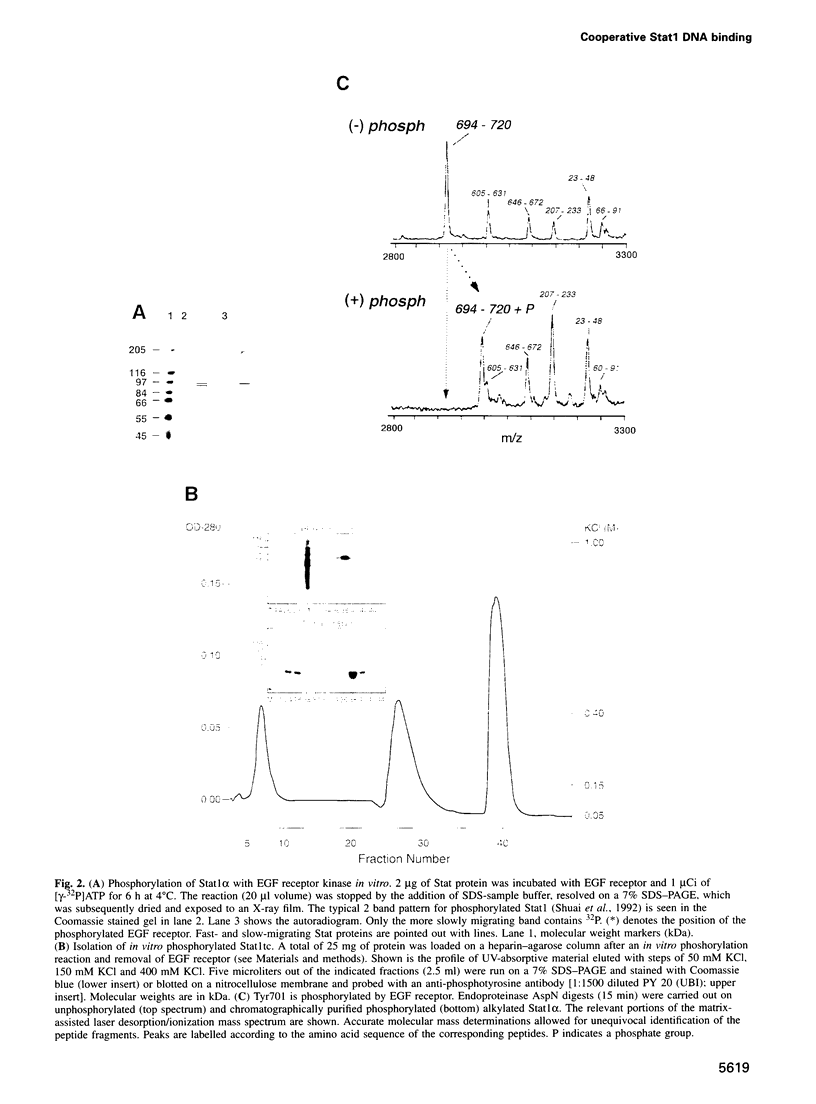
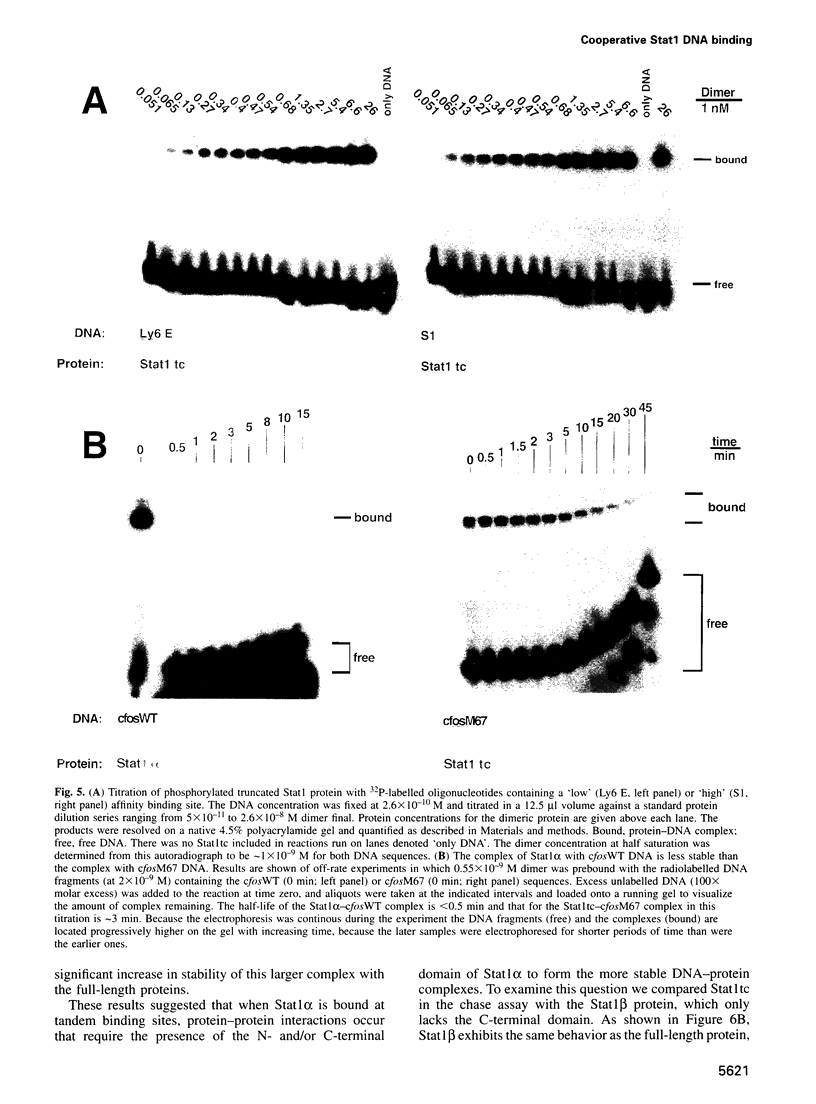
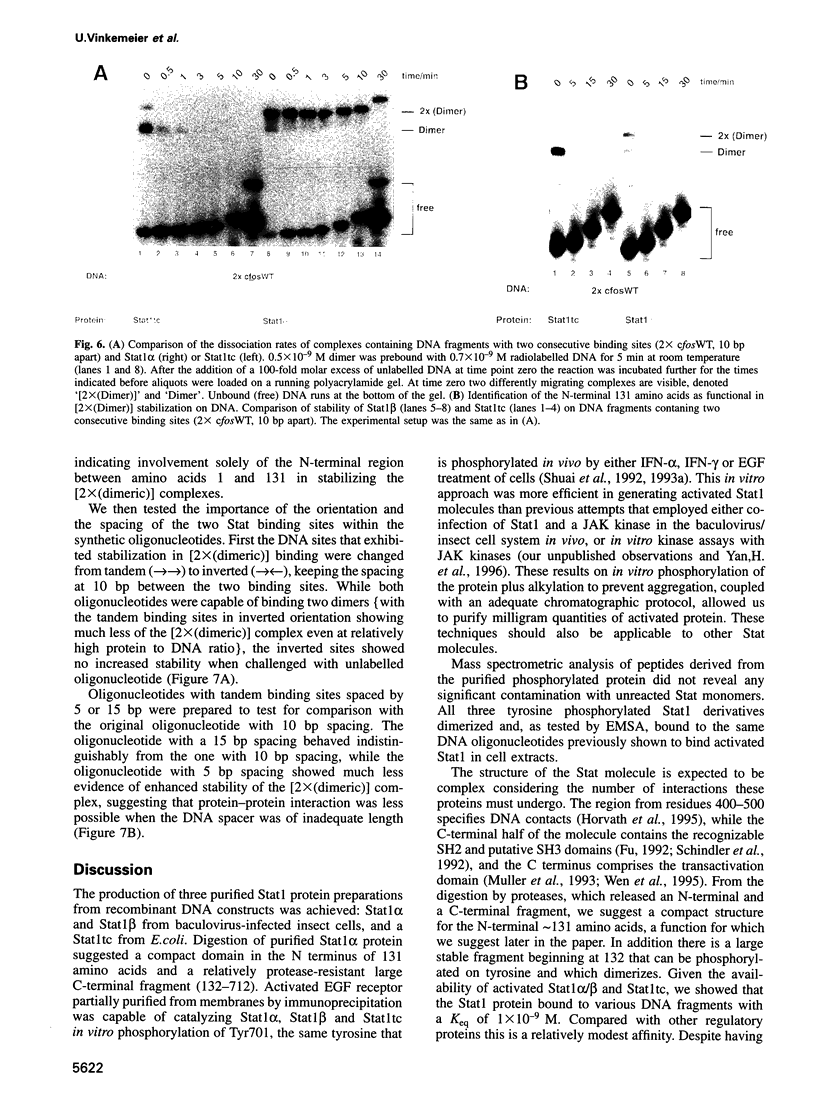
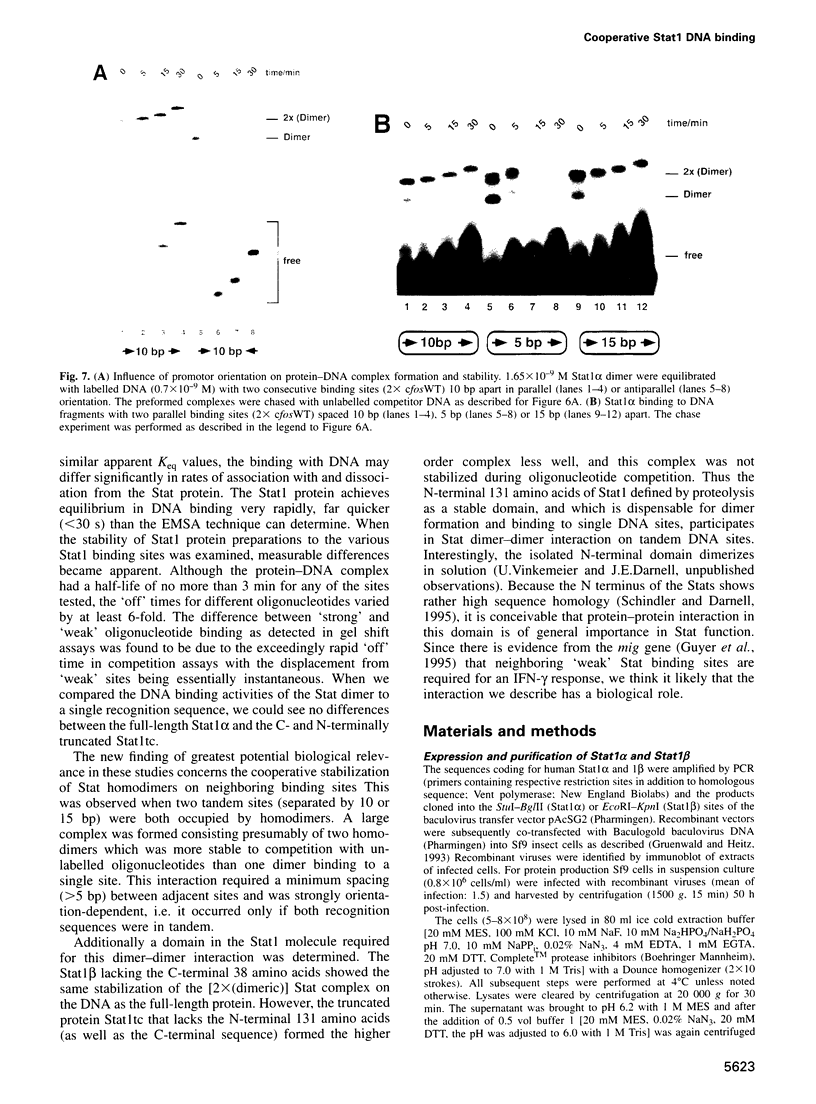
Stat1 alpha, Stat1 beta and a proteolytically defined truncated Stat1 (132-713, Stat1tc) have been prepared from recombinant sources. All three proteins were specifically phosphorylated on Tyr701 in vitro and the phosphoprotein purified to homogeneity. This was achieved by employing a new isolation scheme that does not include DNA affinity steps and readily allows for the isolation of tens of milligrams of activated Stat protein. The purified phosphoprotein was free of traces of unphosphorylated polypeptide as detected by mass spectrometry. The phosphorylated Stat1 preparations bound to various DNA recognition sites with the same Keq of approximately 1 x 10(-9) M; distinction between 'weak' and 'strong' binding sites is determined by the very rapid dissociation (< 30 s, t1/2) from 'weak' sites compared with 'strong' sites (approximately 3 min, t1/2). Reports of 'weak' tandem binding sites in a natural gene caused us to examine binding to tandem sites leading to the finding that the Stat1 alpha or beta (38 amino acids shorter on the C terminus) bound to two tandem sites (but not two head-to-head sites) with a higher stability than to a single recognition site. The N-terminally truncated protein Stat1tc did not show this cooperative binding, thus implicating the N-terminal domain in promoting Stat1-Stat1 dimer interaction.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Affolter M., Percival-Smith A., Müller M., Leupin W., Gehring W. J. DNA binding properties of the purified Antennapedia homeodomain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jun;87(11):4093–4097. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.11.4093. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen S. L., Chait B. T. Influence of matrix solution conditions on the MALDI-MS analysis of peptides and proteins. Anal Chem. 1996 Jan 1;68(1):31–37. doi: 10.1021/ac9507956. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen S. L., Ferré-D'Amaré A. R., Burley S. K., Chait B. T. Probing the solution structure of the DNA-binding protein Max by a combination of proteolysis and mass spectrometry. Protein Sci. 1995 Jun;4(6):1088–1099. doi: 10.1002/pro.5560040607. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darnell J. E., Jr, Kerr I. M., Stark G. R. Jak-STAT pathways and transcriptional activation in response to IFNs and other extracellular signaling proteins. Science. 1994 Jun 3;264(5164):1415–1421. doi: 10.1126/science.8197455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fried M., Crothers D. M. Equilibria and kinetics of lac repressor-operator interactions by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Dec 11;9(23):6505–6525. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.23.6505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fu X. Y. A transcription factor with SH2 and SH3 domains is directly activated by an interferon alpha-induced cytoplasmic protein tyrosine kinase(s). Cell. 1992 Jul 24;70(2):323–335. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90106-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garner M. M., Revzin A. A gel electrophoresis method for quantifying the binding of proteins to specific DNA regions: application to components of the Escherichia coli lactose operon regulatory system. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jul 10;9(13):3047–3060. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.13.3047. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guyer N. B., Severns C. W., Wong P., Feghali C. A., Wright T. M. IFN-gamma induces a p91/Stat1 alpha-related transcription factor with distinct activation and binding properties. J Immunol. 1995 Oct 1;155(7):3472–3480. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horvath C. M., Wen Z., Darnell J. E., Jr A STAT protein domain that determines DNA sequence recognition suggests a novel DNA-binding domain. Genes Dev. 1995 Apr 15;9(8):984–994. doi: 10.1101/gad.9.8.984. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ihle J. N. Cytokine receptor signalling. Nature. 1995 Oct 19;377(6550):591–594. doi: 10.1038/377591a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LeGendre N., Matsudaira P. Direct protein microsequencing from Immobilon-P Transfer Membrane. Biotechniques. 1988 Feb;6(2):154–159. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy D. E., Kessler D. S., Pine R., Darnell J. E., Jr Cytoplasmic activation of ISGF3, the positive regulator of interferon-alpha-stimulated transcription, reconstituted in vitro. Genes Dev. 1989 Sep;3(9):1362–1371. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.9.1362. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller M., Laxton C., Briscoe J., Schindler C., Improta T., Darnell J. E., Jr, Stark G. R., Kerr I. M. Complementation of a mutant cell line: central role of the 91 kDa polypeptide of ISGF3 in the interferon-alpha and -gamma signal transduction pathways. EMBO J. 1993 Nov;12(11):4221–4228. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb06106.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quelle F. W., Thierfelder W., Witthuhn B. A., Tang B., Cohen S., Ihle J. N. Phosphorylation and activation of the DNA binding activity of purified Stat1 by the Janus protein-tyrosine kinases and the epidermal growth factor receptor. J Biol Chem. 1995 Sep 1;270(35):20775–20780. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.35.20775. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qureshi S. A., Salditt-Georgieff M., Darnell J. E., Jr Tyrosine-phosphorylated Stat1 and Stat2 plus a 48-kDa protein all contact DNA in forming interferon-stimulated-gene factor 3. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Apr 25;92(9):3829–3833. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.9.3829. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riggs A. D., Suzuki H., Bourgeois S. Lac repressor-operator interaction. I. Equilibrium studies. J Mol Biol. 1970 Feb 28;48(1):67–83. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90219-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schindler C., Darnell J. E., Jr Transcriptional responses to polypeptide ligands: the JAK-STAT pathway. Annu Rev Biochem. 1995;64:621–651. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.64.070195.003201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schindler C., Fu X. Y., Improta T., Aebersold R., Darnell J. E., Jr Proteins of transcription factor ISGF-3: one gene encodes the 91-and 84-kDa ISGF-3 proteins that are activated by interferon alpha. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Aug 15;89(16):7836–7839. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.16.7836. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shuai K., Horvath C. M., Huang L. H., Qureshi S. A., Cowburn D., Darnell J. E., Jr Interferon activation of the transcription factor Stat91 involves dimerization through SH2-phosphotyrosyl peptide interactions. Cell. 1994 Mar 11;76(5):821–828. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90357-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shuai K., Schindler C., Prezioso V. R., Darnell J. E., Jr Activation of transcription by IFN-gamma: tyrosine phosphorylation of a 91-kD DNA binding protein. Science. 1992 Dec 11;258(5089):1808–1812. doi: 10.1126/science.1281555. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shuai K., Stark G. R., Kerr I. M., Darnell J. E., Jr A single phosphotyrosine residue of Stat91 required for gene activation by interferon-gamma. Science. 1993 Sep 24;261(5129):1744–1746. doi: 10.1126/science.7690989. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shuai K., Ziemiecki A., Wilks A. F., Harpur A. G., Sadowski H. B., Gilman M. Z., Darnell J. E. Polypeptide signalling to the nucleus through tyrosine phosphorylation of Jak and Stat proteins. Nature. 1993 Dec 9;366(6455):580–583. doi: 10.1038/366580a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studier F. W., Moffatt B. A. Use of bacteriophage T7 RNA polymerase to direct selective high-level expression of cloned genes. J Mol Biol. 1986 May 5;189(1):113–130. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90385-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner B. J., Hayes T. E., Hoban C. J., Cochran B. H. The SIF binding element confers sis/PDGF inducibility onto the c-fos promoter. EMBO J. 1990 Dec;9(13):4477–4484. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07898.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wen Z., Zhong Z., Darnell J. E., Jr Maximal activation of transcription by Stat1 and Stat3 requires both tyrosine and serine phosphorylation. Cell. 1995 Jul 28;82(2):241–250. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90311-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yan H., Krishnan K., Greenlund A. C., Gupta S., Lim J. T., Schreiber R. D., Schindler C. W., Krolewski J. J. Phosphorylated interferon-alpha receptor 1 subunit (IFNaR1) acts as a docking site for the latent form of the 113 kDa STAT2 protein. EMBO J. 1996 Mar 1;15(5):1064–1074. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yan R., Qureshi S., Zhong Z., Wen Z., Darnell J. E., Jr The genomic structure of the STAT genes: multiple exons in coincident sites in Stat1 and Stat2. Nucleic Acids Res. 1995 Feb 11;23(3):459–463. doi: 10.1093/nar/23.3.459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yan R., Small S., Desplan C., Dearolf C. R., Darnell J. E., Jr Identification of a Stat gene that functions in Drosophila development. Cell. 1996 Feb 9;84(3):421–430. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)81287-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yarden Y., Harari I., Schlessinger J. Purification of an active EGF receptor kinase with monoclonal antireceptor antibodies. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jan 10;260(1):315–319. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]