Fig 8. Inflammation plays a key-role in the genesis of anemia in CKD.
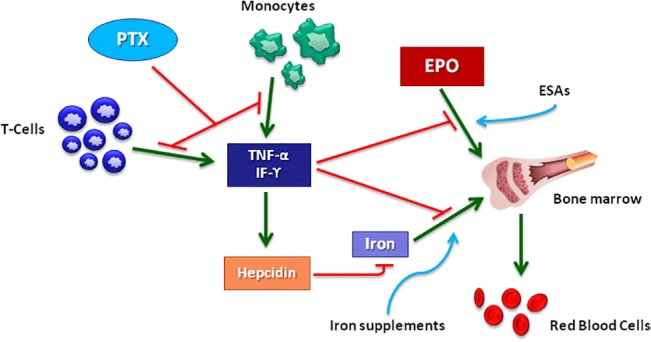
TNF-α and IF-ϒ are pro-inflammatory cytokines which may generate or worsen anemia by limiting the pro-erythropoietic effect of EPO and ESAs at the medullary level. In addition, such cytokines may reduce iron bio-availability by increasing serum hepcidin levels. Pentoxifylline would improve anemia in CKD by inhibiting the release of TNF-α and IF-ϒ from monocytes and T-cells. This would ameliorate the medullary sensitivity to endogenous EPO and exogenous ESAs and reduce the need for iron supplements by increasing endogenous iron availability. Legend to Fig 8: PTX: pentoxifylline, TNF-α: tumor necrosis factor alpha, EPO: erythropoietin, ESAs: erythropoiesis stimulating agents, IF-ϒ: interferon gamma
