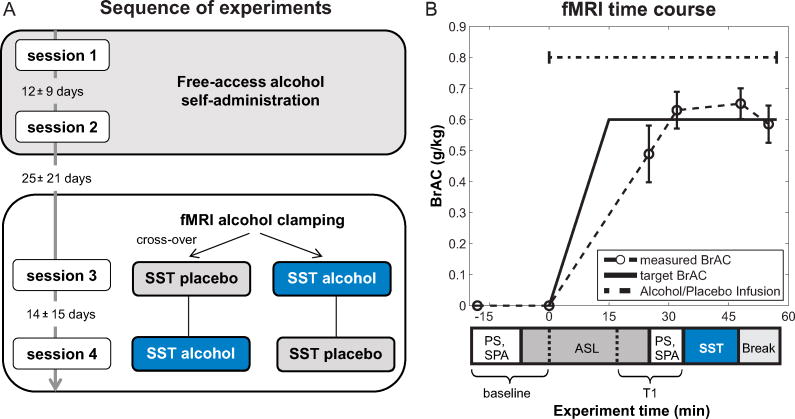
Figure 1.
Sequence of experiments and fMRI time course. A: The experiment consisted of four sessions. First, we conducted free-access alcohol self-administration on two separate days (session 1+2). Second, the SST was performed during fMRI alcohol clamping, once under a constant alcohol exposure of 0.6 g/kg, and once under placebo (session 3+4). The order of the alcohol and placebo condition in the fMRI alcohol clamping part was randomized across participants. B: Timing of the fMRI alcohol clamping experiment with target and measured BrACs (mean, Error bars represent standard deviations). We also measured subjective perceptions of alcohol (SPA) and saccadic eye-movements (PS) at baseline and before the SST at T1 to track the “Level of alcohol intoxication” (see supplement). After the break, the experiment continued with other tasks (see supplement Figure S1 for complete time course). Abbreviations: ASL = arterial spin labeling, BrAC = breath alcohol concentration, PS = prosaccades, SPA = subjective perception of alcohol, SST = stop-signal task, T1 = time 1.