Fig 1.
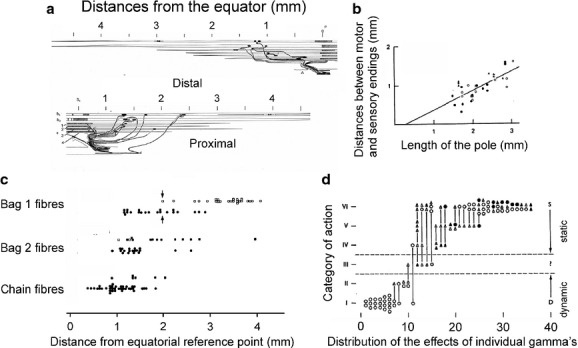
Contacts and actions of feline fusimotor neurons. (a) Reconstruction of contacts of fusimotor fibres innervating the two poles of a muscle spindle illustrating the range of distances (approximately 1.5–2.5 mm) from the equator at which these contacts were formed. (b) Plot of distances between the centres of the motor and sensory endings (ordinate) against the length of the intrafusal muscle fibre pole, taking the centre of the primary ending as the equatorial limit, illustrating an even larger range of distances from the equator. (c) Distribution of foci of contractions evoked by single fusimotor fibres from the equatorial reference point. (d) The range of action exerted by a sample of 37 feline individual fusimotor fibres on different primary endings. The strongest static actions correspond to category VI and the strongest dynamic actions to category I, the symbols indicating fusimotor actions on two–five primary endings. (a and b) Modified from figs 1 and 5 in Banks (1981); (c) from fig. 2 in Banks et al. (1978); (d) from fig. 14 in Emonet-Denand et al. (1977). In this and in the following figures, all reproductions are with permission.
