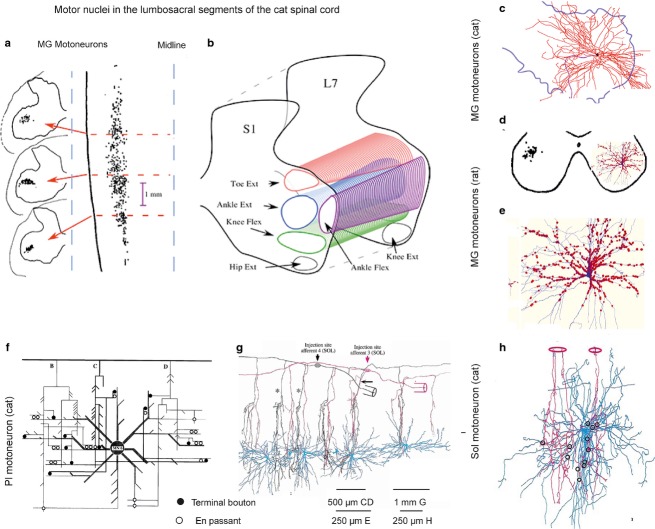
Fig 3.
Synaptic contacts between muscle spindle primaries and motoneurons. (a) Retrogradely labelled cell bodies of feline medial gastrocnemius (MG) motoneurons in three transverse planes (left) and in a horizontal plane (right). (b) Columns of feline hindlimb motor nuclei in a transverse plane. (c and d) Dendritic trees of two MG motoneurons overlying most of the ventral horn area in the cat and the rat, respectively. (e) Expanded dendritic tree of the motoneuron in (d) (in blue) with contacts of VGLUT1-IR terminals (red) representing contacts of muscle spindle afferents, mainly primaries but perhaps also secondaries. These are the only peripheral afferents synapsing with alpha motoneurons. (f) Wiring diagram of contacts between three adjacent feline plantaris (Pl) afferent collaterals and dendrites of a Pl motoneuron. (g) Reconstruction of the trajectory of axon collaterals of two feline soleus Ia afferents crossing dendritic trees of six motoneurons at different distances from their cell bodies in a sagittal plane. (h) Reconstruction of contacts of two feline soleus afferent collaterals with a soleus (Sol) motoneuron. (a–c) From figs 1 and 3 in Burke (2013); (d, e) from fig. 4 in Rotterman et al. (2014); (f–h) from figs 1, 2 and 8 in Burke & Glenn (1996).