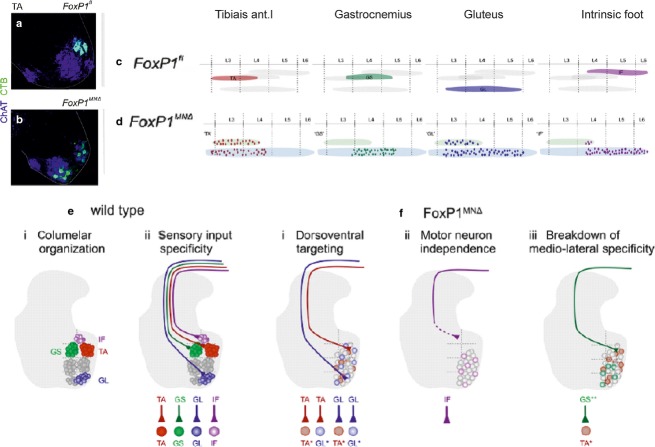
Fig 4.
Changes in the connectivity between group Ia afferents and motoneurons related to the dislocation of the motoneurons. (a and b) Positions of tibialis anterior (TA) motoneurons labelled by retrograde transport of cholera toxin B (CTB, light green) in a wild-type mouse preparation and in a mouse mutant in which FoxP1 protein was absent in motoneurons. (c and d) As in (a and b), but showing rostrocaudal distribution of four motoneuron pools. (e) Diagrams of motor columns in wild-type mice and of selective coupling between group Ia afferents and homonymous motoneurons. (f) Diagrams illustrating breakdown in specific connections between Ia afferents and motoneurons after the dislocation of motor nuclei in the FoxP1 mutant. Modified from figs 2, 4 and 7 in Surmeli et al. (2011). ChAT, choline acetyltransferase; GL, gluteus; GS, gastrocnemius; IF, intrinsic foot.