Fig 1.
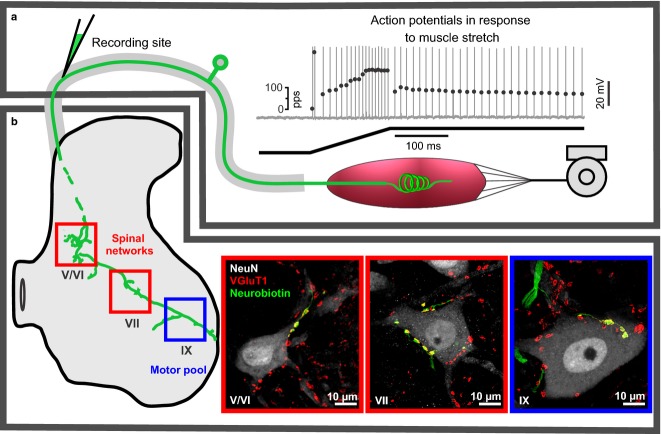
Diagram and data representing selected functions and structures of IA afferent in adult rat. (a and b) This IA afferent is divided, respectively, into peripheral and central portions relative to micropipette recording site in dorsal root near its spinal cord entry zone. (a) IA afferent firing that is produced in response to ramp-hold muscle stretch and that represents the culmination of mechanical transduction followed by action potential encoding and orthodromic conduction. Top trace shows action potentials vertical lines with instantaneous firing rates plotted by superimposed black dots; the bottom trace is muscle length during ramp-hold stretch (ramp 20 mm/s to 3 mm and hold for 1 s). (b) Central IA afferent structures, including central axon collaterals (intra-axonal neurobiotin labeled green) that project in the spinal cord to laminae V/VI, VII, IX where they form synapses (VGluT1) with different populations of neurons (labeled with NeuN). Regions (a and b) are divided to assist discussion of where and how IA afferent demonstrate impairment after peripheral nerve injury and chronic chemotherapy.