Fig. 1.
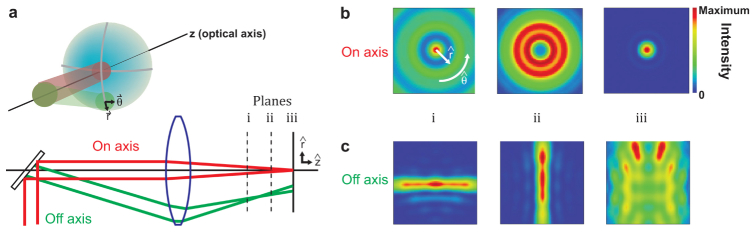
Design issues of the ultra-large-field-of-view two-photon scanning microscope. (a) Illustration of scan-induced aberrations through a spherical singlet lens in a configuration that corresponds to a scan lens. Scanning across a lens maintains on-axis behavior in the direction perpendicular to the scan, yet results in off-axis behavior along the scan dimension, with a reduced effective focal length at increasing off-axis scan angles. (b,c) The on-axis scan beam (red rays) converges at the paraxial focal plane (plane iii, which would be conjugate to the sample plane in a scanning microscope) but the off-axis scan beam (green rays) converges closer to the lens with separate horizontal (plane i) and vertical foci (plane ii). The focal plane intensity maps explicitly show the resulting astigmatism. An intensity of exactly one is the diffraction limited peak value; the maximums for panel b are i: 0.016, ii: 0.035, and iii: 1.000 and those for panel c are i: 0.134, ii: 0.114, and iii: 0.014.
