Fig. 7.
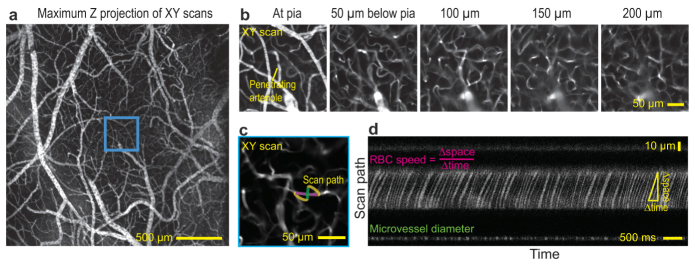
Volumetric two-photon imaging (λ0 = 800 nm) of the vasculature in one hemisphere of mouse cortex. Blood plasma is stained with fluorescein dextran. (a) Cortical vasculature through a thin skull window that is projected over 210 µm. (b) Descending planar images at different depths within the cyan box in panel a. Each image is the average of ten optical sections. The depth is limited by the laser power, 80 mW at the focus. (c) The expanded field within the cyan box in panel a shows a single planar field acquired at a depth of 110 µm below the pial surface and a scan path for functional imaging of blood flow. The segment along the vessel (magenta) tracks individual RBCs and that perpendicular to the vessel (green) reports the diameter. (d) Scan path imaging through the capillary. At mid-height in image, the broad segment with dark streaks indicate the passing of RBCs; the speed of the RBCs is inferred from the slop of the streaks. The thin segment in the lower portion of the image reports the diameter of the vessel.
