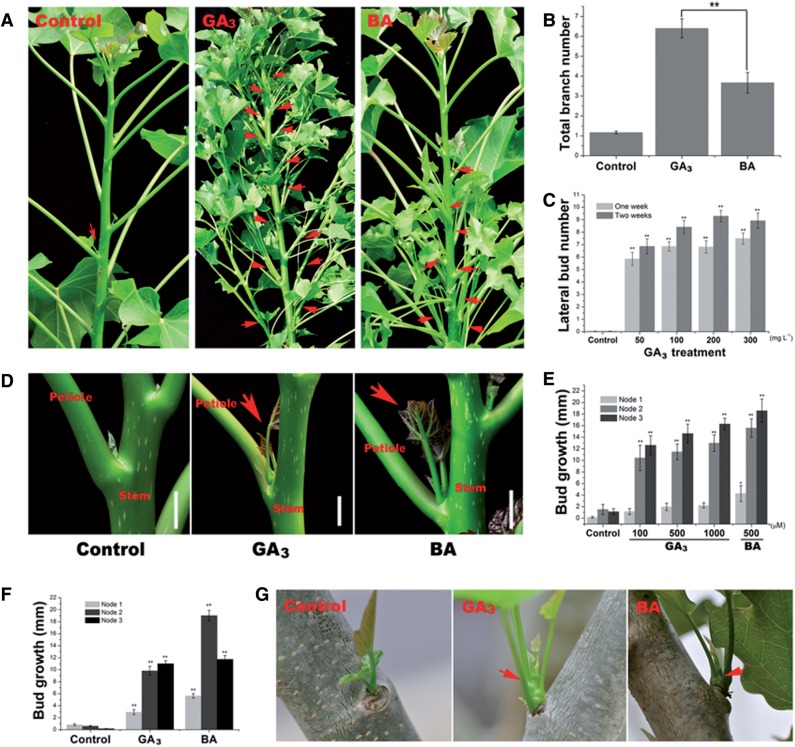
Fig. 1.
GA3 and BA promote shoot branching in J. curcas. (A) Shoot branching stimulated by GA3 or BA treatment in the young stems of 2-year-old J. curcas trees. (B) The number of induced branches was counted 4 weeks after GA3 (500 mg l–1) or BA (500 mg l–1) treatment (n = 30). (C) The number of stimulated axillary buds was counted 1 and 2 weeks after the application of various concentrations of GA3 to the top region of the branch (∼20 cm; n = 28–45). (D) Representative lateral bud stimulated by GA3 treatment in 2-year-old J. curcas trees. (E) Axillary bud length at nodes 1–3 of 4-week-old J. curcas seedlings measured 2 weeks after GA3 or BA treatment (n = 12–14). (F) Buds at nodes 1–3 of 5-week-old J. curcas seedlings showed different responsiveness to GA3 or BA (500 μM) treatment (n > 20). (G) Lateral bud on an old stem of a 3-year-old J. curcas tree, stimulated by GA3 or BA (500 μM) treatment. Values are means ± SE for (B), (C), (E) and (F). Student’s t-test was used to determine significant differences between the indicated groups in (B) or between the treated and control groups in (C), (E) and (F). Significance levels: *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01. Red arrows indicate the stimulated axillary buds.