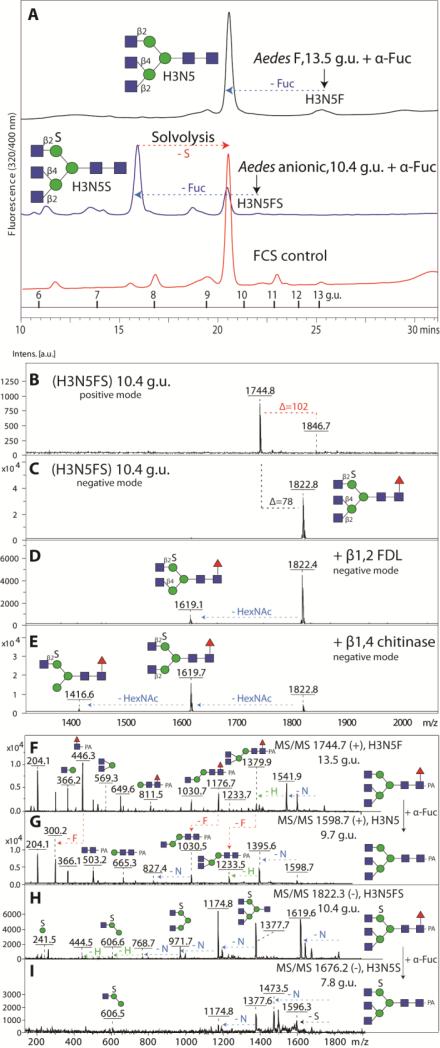
Figure 4. Elucidation of neutral and anionic triantennary N-glycan structures.
(A) Coelution of Aedes derived triantennary glycans after either defucosylation of the neutral glycan species or solvolysis and defucosylation of the sulphated glycan species with an asialoagalacto-triantennary N-glycan isolated from FCS; note that solvolysis under these conditions is incomplete, but that further incubation resulted in unspecific reaction products. The arrows indicate the shifts in retention time. MALDI TOF/TOF MS spectra in positive (B) and negative ion mode (C-E) of the Aedes anionic triantennary structure eluting at 10.4 g.u. on RP-Amide HPLC show that the anionic triantennary structure is sensitive to β1,2-specific FDL (D) and β1,4-specific ‘chitinase-type’ hexosaminidase (E). MS/MS spectra of parent and product glycan species upon bovine fucosidase digests in positive (F, G) and negative ion mode (H, I) are shown.