Figure 2. Prevention of ischemia-induced autophagy in cerebellum using Atg7 siRNA.
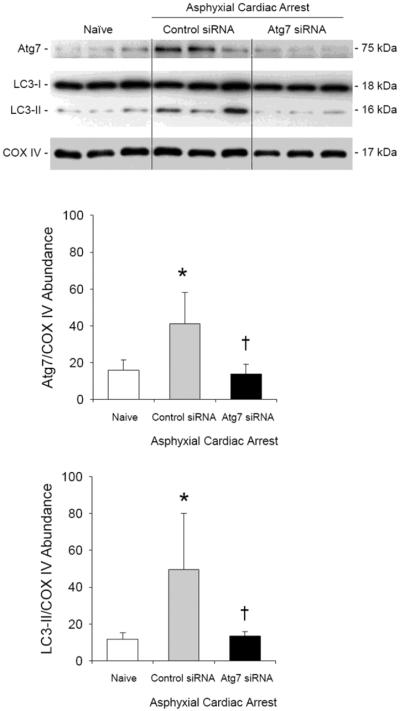
Western blot analysis of LC3-I and LC3-II in cerebellum of naïve male rats and male rats 24 h after asphyxial cardiac arrest. At 48 h before asphyxial arrest, rats were randomized to receive control or Atg7 siRNA via intracisternal injection. In rats treated with control siRNA, relative LC3-II protein abundance adjusted for cytochrome oxidase IV (COX IV) as a loading control increased after asphyxial cardiac arrest vs. naïve rats (*P < 0.05). Treatment with Atg7 siRNA prevented an ischemia-induced increase in LC3-II:COX IV vs. control siRNA. Consistent with Fig. 2, Atg7:COX IV ratios were also reduced in Atg7 vs. control siRNA treated rats after asphyxia. Mean ± SD, n = 3/group, *P < 0.05 vs. naïve, †P < 0.05 vs. control siRNA, ANOVA with Tukey's post hoc test.
